Original paper
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Re-infection by a Phylogenetically Distinct Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Strain Confirmed by Whole Genome Sequencing
Abstract
Waning immunity occurs in patients who have recovered from Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, it remains unclear whether true re-infection occurs.Whole genome sequencing was performed directly on respiratory specimens collected during 2 episodes of COVID-19 in a patient. Comparative genome analysis was conducted to differentiate re-infection from persistent viral shedding. Laboratory results, including RT-PCR Ct values and serum...
Figures & Tables
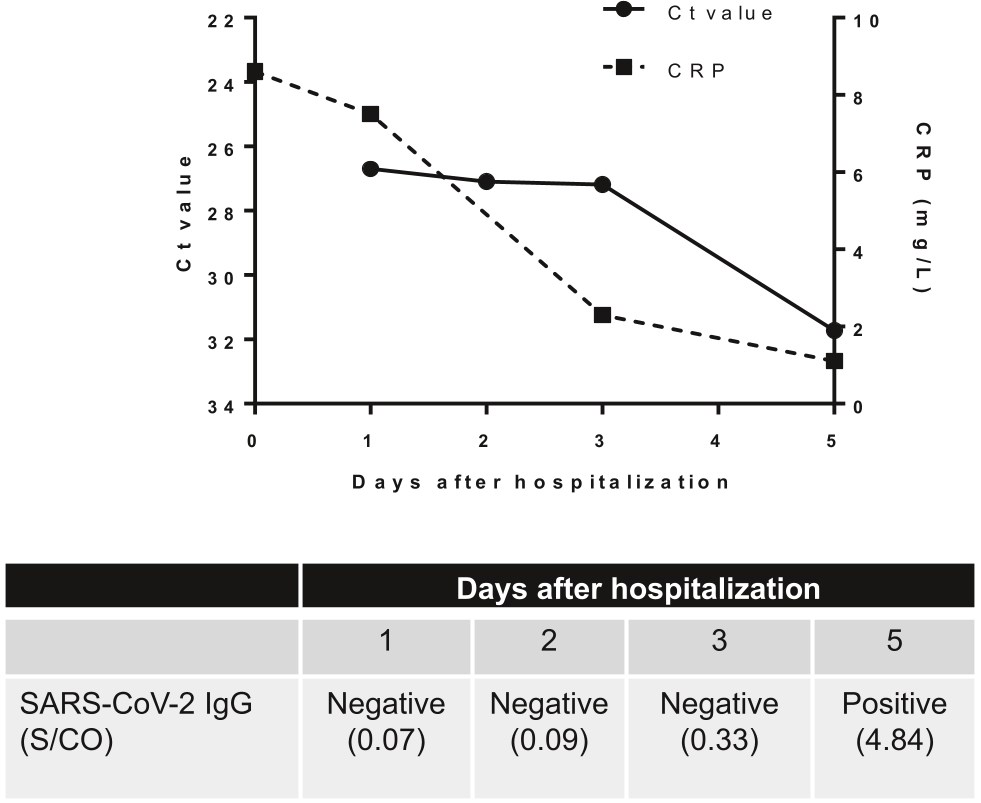
Figure 1. Serial C-reactive protein level, viral load (Ct value), and SARS-CoV-2...

Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of whole SARS-CoV-2 genomes showing the relation...
Paper Details
Title
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Re-infection by a Phylogenetically Distinct Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Strain Confirmed by Whole Genome Sequencing
Published Date
Aug 24, 2020
Journal
Volume
73
Issue
9
Pages
e2946 - e2951
TrendsPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand a paper’s academic impact over time?
- Scinapse’s Citation Trends graph enables the impact assessment of papers in adjacent fields.
- Assess paper quality within the same journal or volume, irrespective of the year or field, and track the changes in the attention a paper received over time.
Citation AnalysisPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand the true influence of a researcher’s work across journals & affiliations?
- Scinapse’s Top 10 Citation Journals & Affiliations graph reveals the quality and authenticity of citations received by a paper.
- Discover whether citations have been inflated due to self-citations, or if citations include institutional bias.