Original paper
Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine
Abstract
The outbreak of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has posed a serious threat to global public health, calling for the development of safe and effective prophylactics and therapeutics against infection of its causative agent, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), also known as 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). The CoV spike (S) protein plays the most important roles in viral attachment, fusion and entry, and serves as...
Figures & Tables
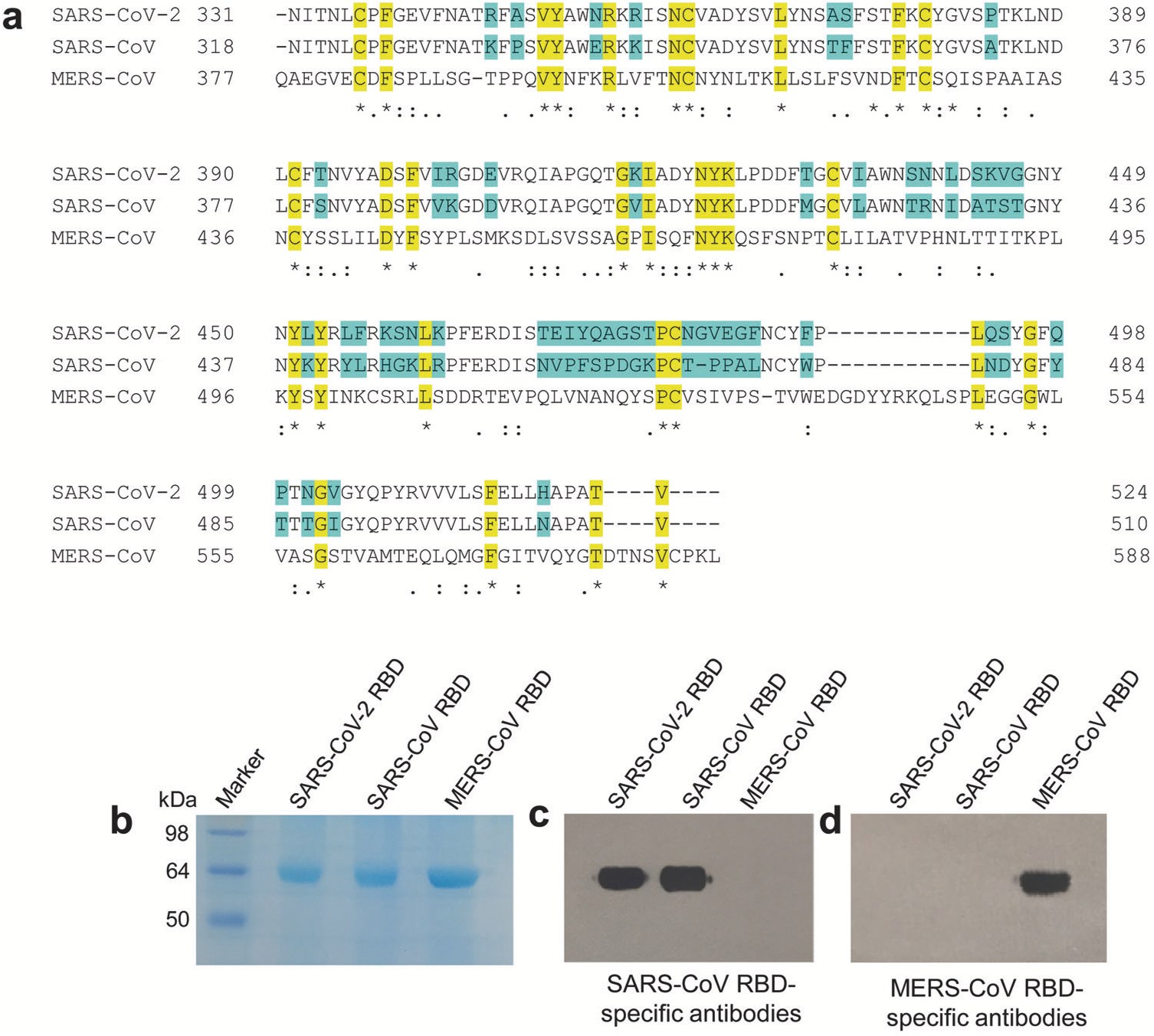
Fig. 1 Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 RBD. a Multiple sequence alignment of RBDs...
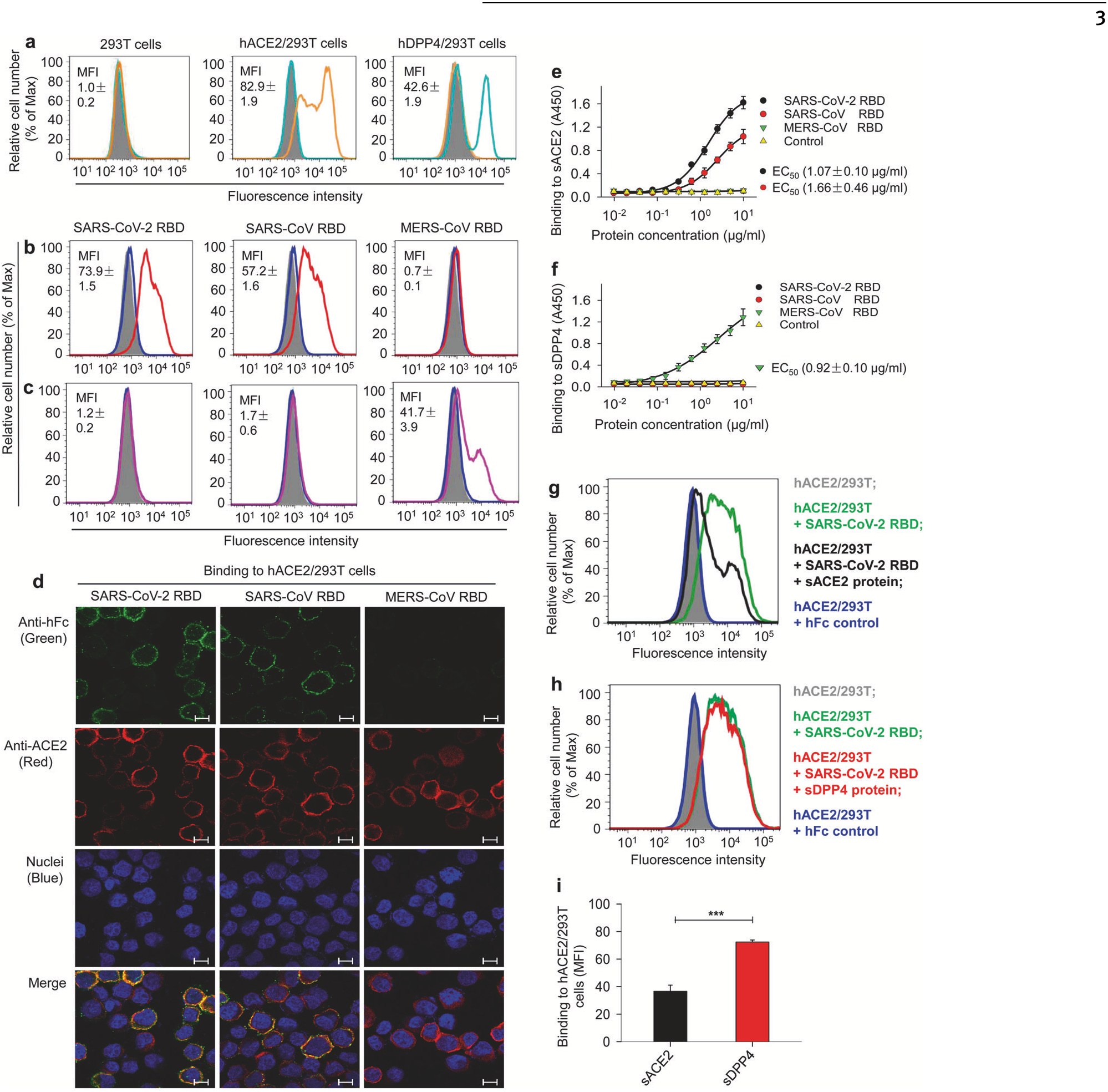
Fig. 2 Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RBD binding to human ACE2 receptor. a Flow cytome...
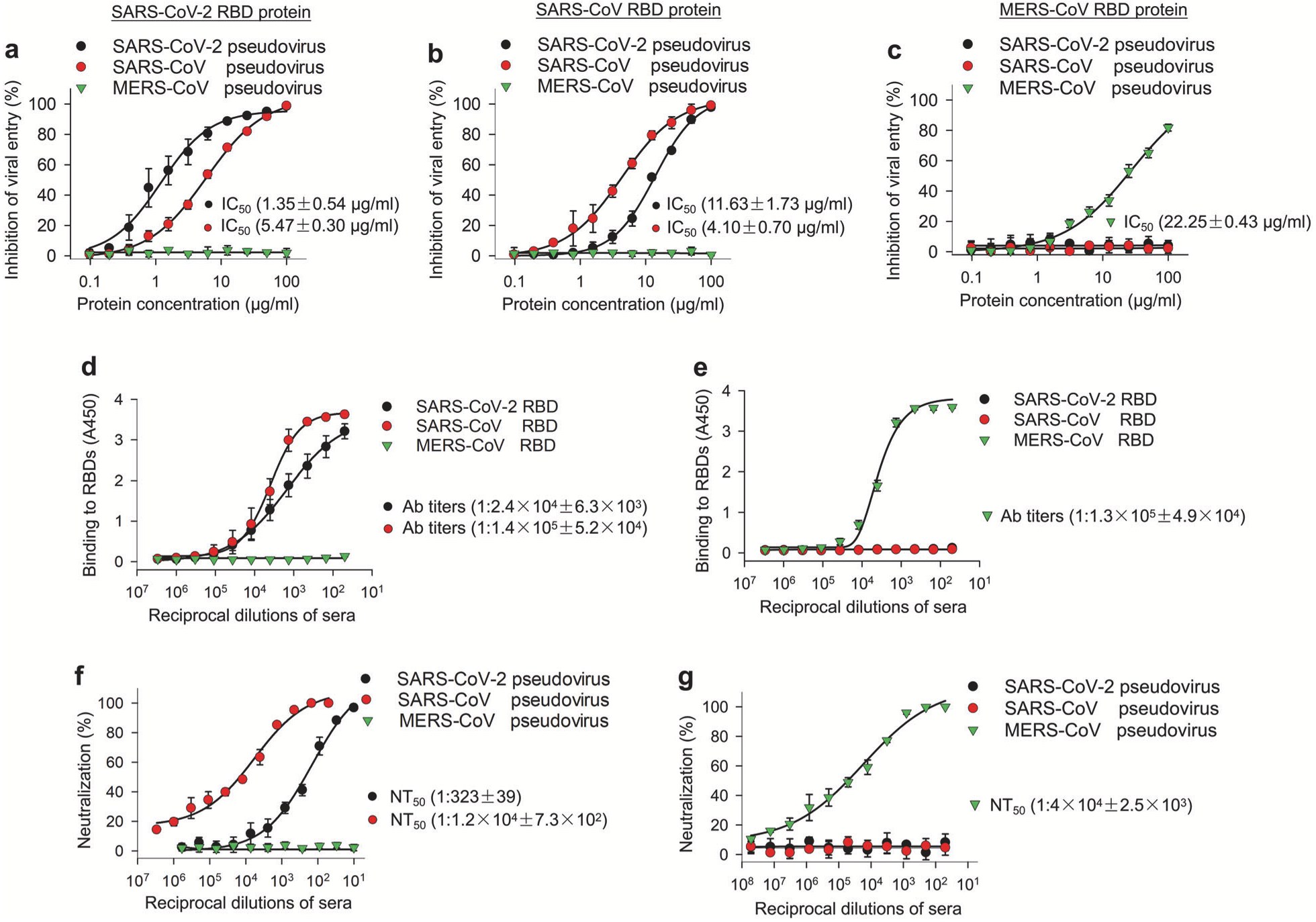
Fig. 4 Ability of SARS-CoV-2 RBD to inhibit viral entry, as well as its cross-re...
Paper Details
Title
Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine
Published Date
Mar 19, 2020
Volume
17
Issue
6
Pages
613 - 620
TrendsPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand a paper’s academic impact over time?
- Scinapse’s Citation Trends graph enables the impact assessment of papers in adjacent fields.
- Assess paper quality within the same journal or volume, irrespective of the year or field, and track the changes in the attention a paper received over time.
Citation AnalysisPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand the true influence of a researcher’s work across journals & affiliations?
- Scinapse’s Top 10 Citation Journals & Affiliations graph reveals the quality and authenticity of citations received by a paper.
- Discover whether citations have been inflated due to self-citations, or if citations include institutional bias.