Original paper
Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016
Abstract
Summary
Background
As mortality rates decline, life expectancy increases, and populations age, non-fatal outcomes of diseases and injuries are becoming a larger component of the global burden of disease. The Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2016 (GBD 2016) provides a comprehensive assessment of prevalence, incidence, and years lived with disability (YLDs) for 328 causes in 195 countries and territories...Figures & Tables
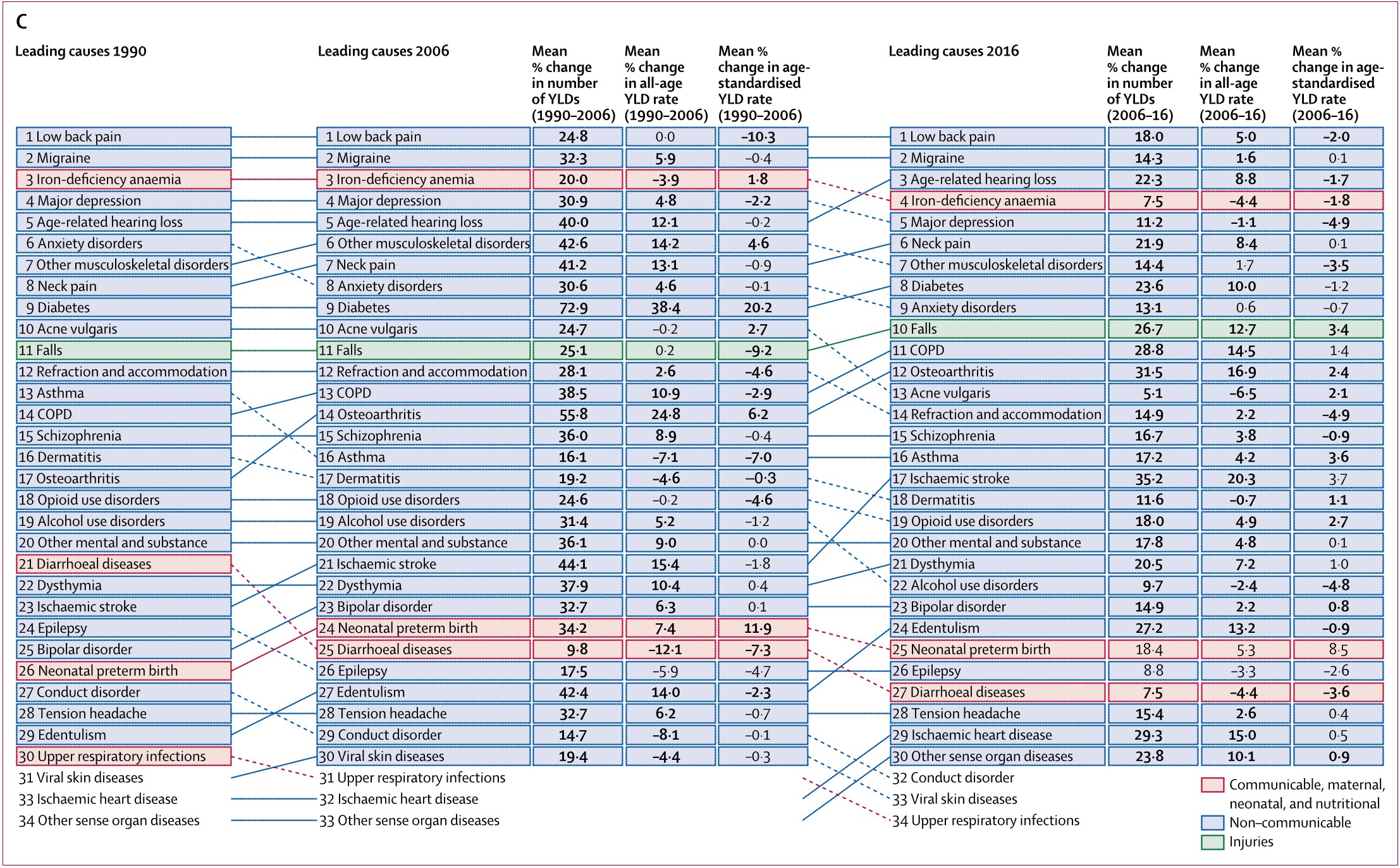
Figure 1: Leading 30 Level 4 causes of global prevalence (A), incidence (B), and...
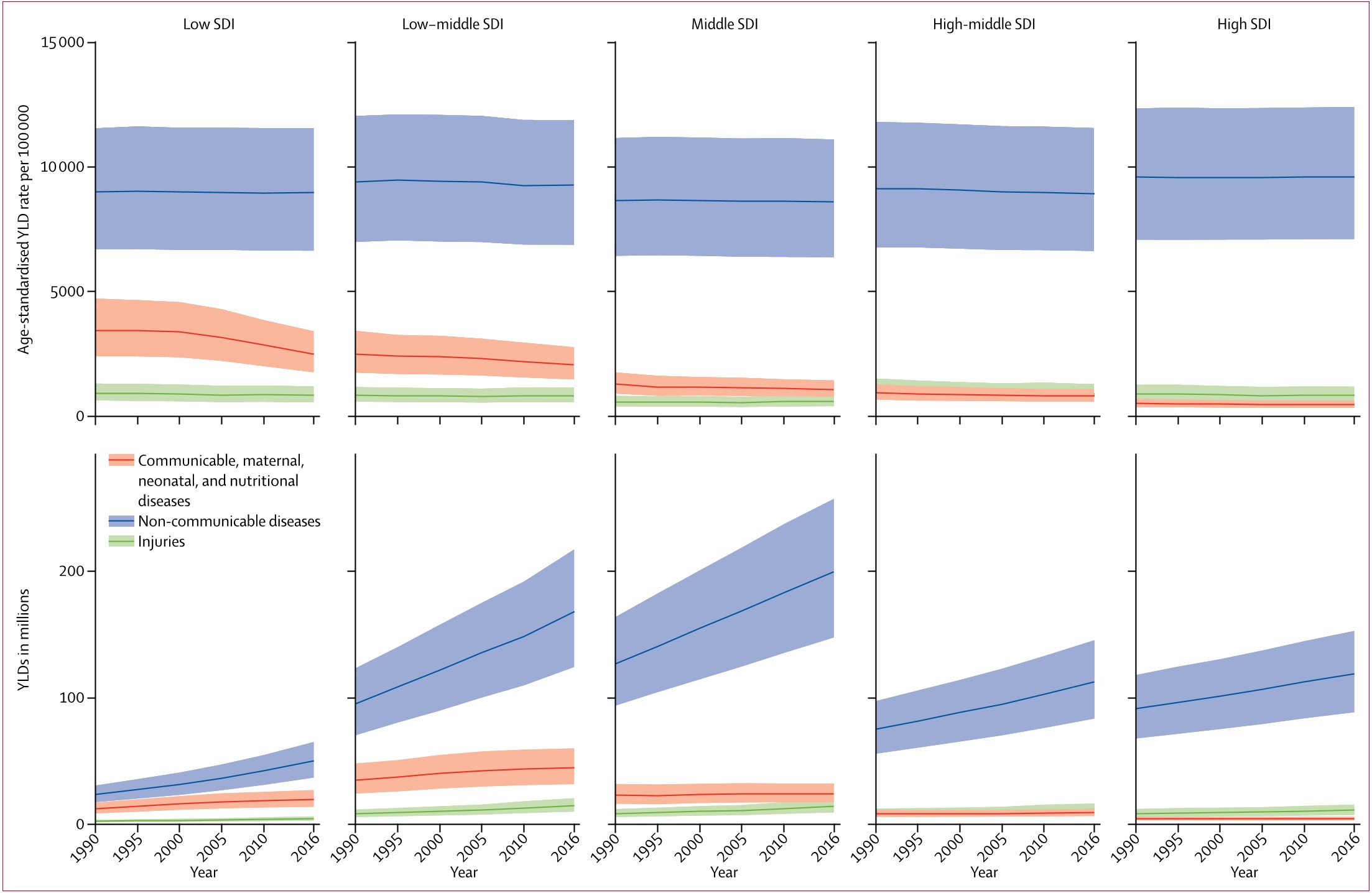
Figure 3: Trends of age-standardised YLD rates per 100 000 and total YLDs from 1...
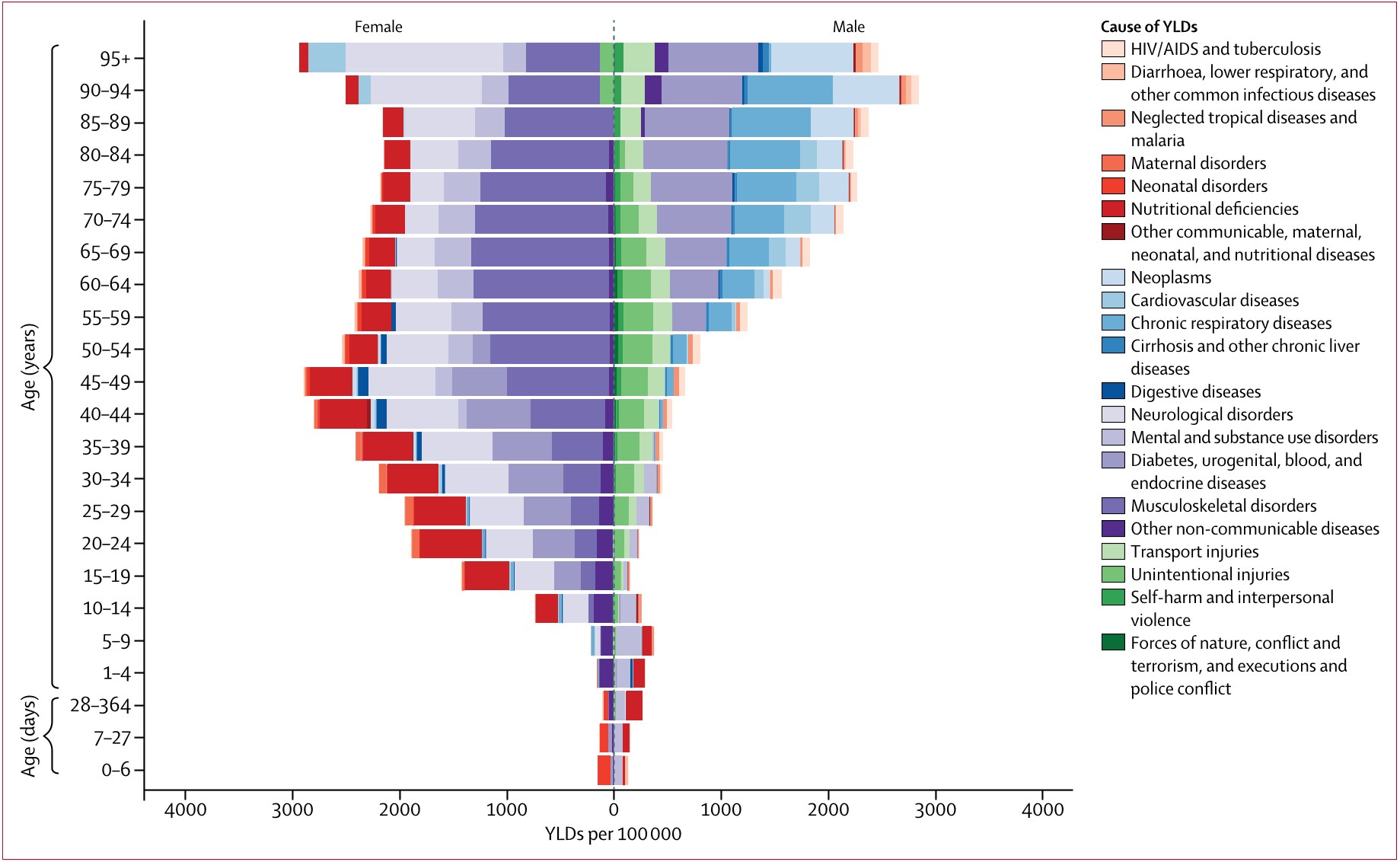
Figure 5: Sex difference in global YLD rates per 100 000 for 21 Level 2 causes b...
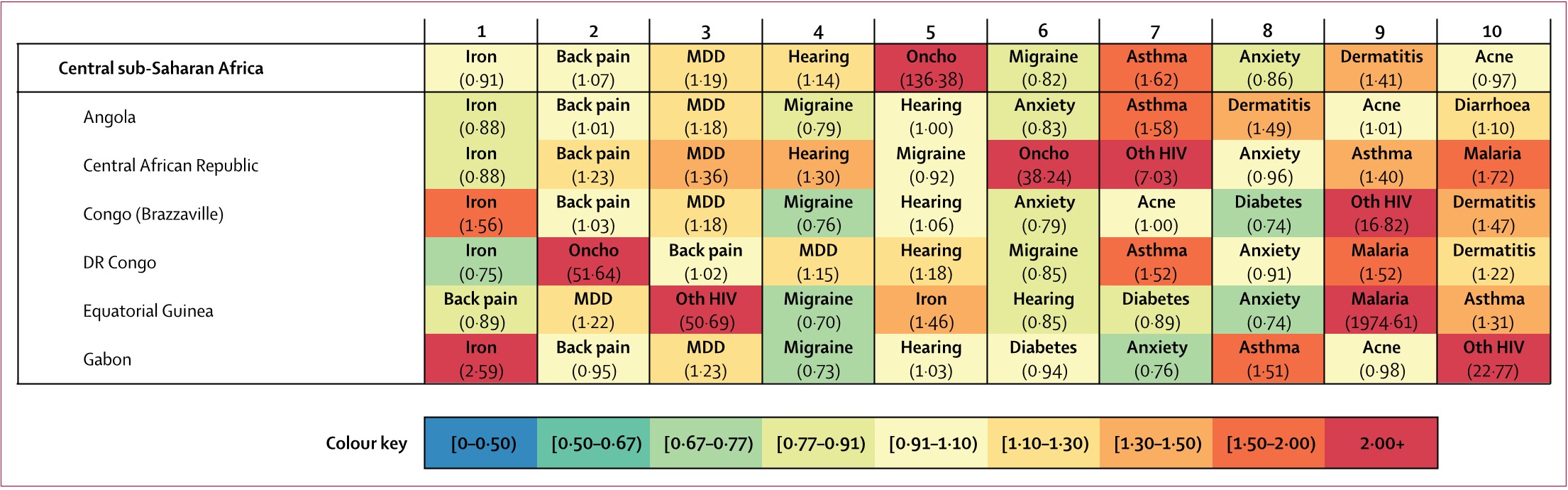
Figure 7: Leading ten causes of YLDs with ratio of observed YLDs to YLDs expecte...
Paper Details
Title
Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016
Published Date
Sep 1, 2017
Journal
Volume
390
Issue
10100
Pages
1211 - 1259
TrendsPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand a paper’s academic impact over time?
- Scinapse’s Citation Trends graph enables the impact assessment of papers in adjacent fields.
- Assess paper quality within the same journal or volume, irrespective of the year or field, and track the changes in the attention a paper received over time.
Citation AnalysisPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand the true influence of a researcher’s work across journals & affiliations?
- Scinapse’s Top 10 Citation Journals & Affiliations graph reveals the quality and authenticity of citations received by a paper.
- Discover whether citations have been inflated due to self-citations, or if citations include institutional bias.