Original paper
Effect of Sappan Wood (Caesalpinnia sappan L) Extract on Blood Glucose Level in White Rats
Volume: 1, Issue: 2, Pages: 109 - 115
Published: Jan 1, 2014
Abstract
Sappan wood or kayu secang (Caesalpinia sappan L.) was reported of having medicinal properties, such as natural antioxidant, relieve vomiting of blood, and mix of ingredients for malaria drugs. The research was conducted to study the influence of ethanol extract from sappan wood on blood glucose level of white rats. The study of the blood glucose level in rats was carried out by using glucose tolerance method. It was measured by Refloluxs...
Figures & Tables
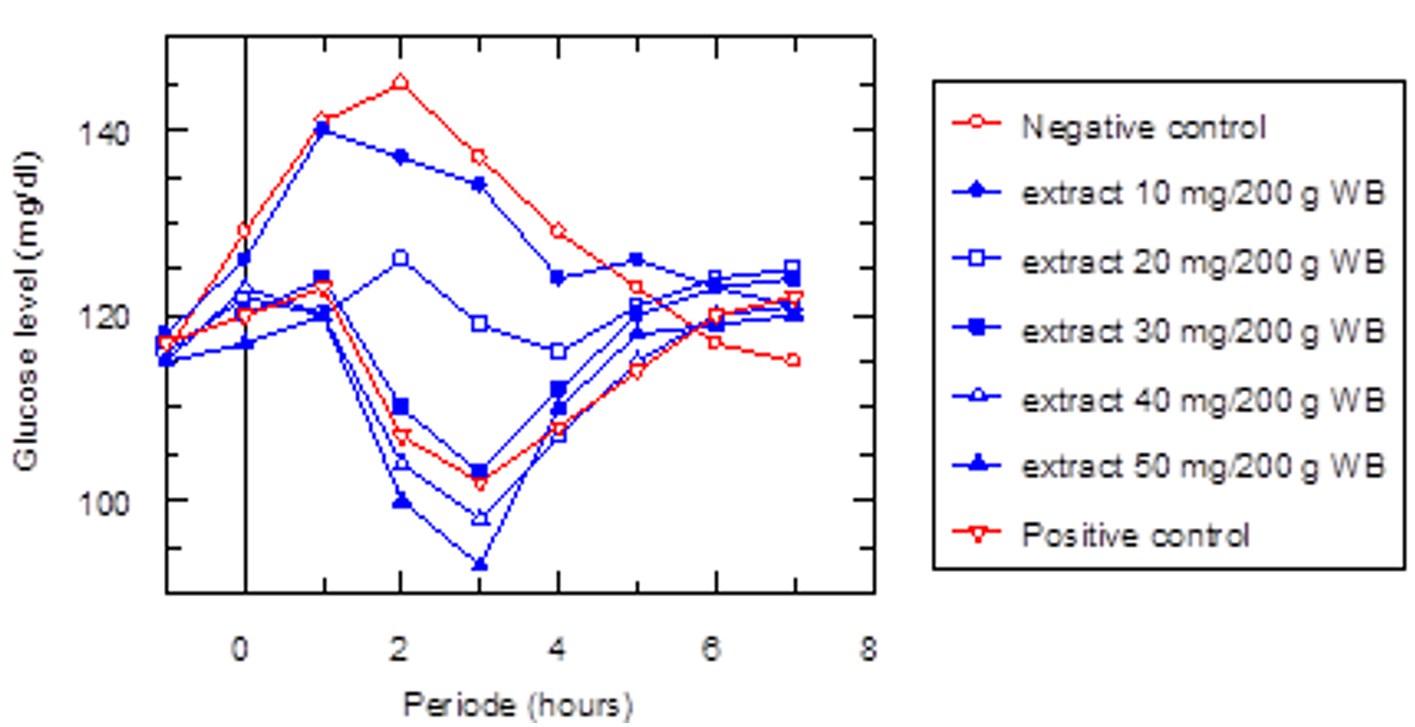
Figure 1. Curve of glucose level in rat blood after treatment

Table 1. Preliminary testing of extract in white rats
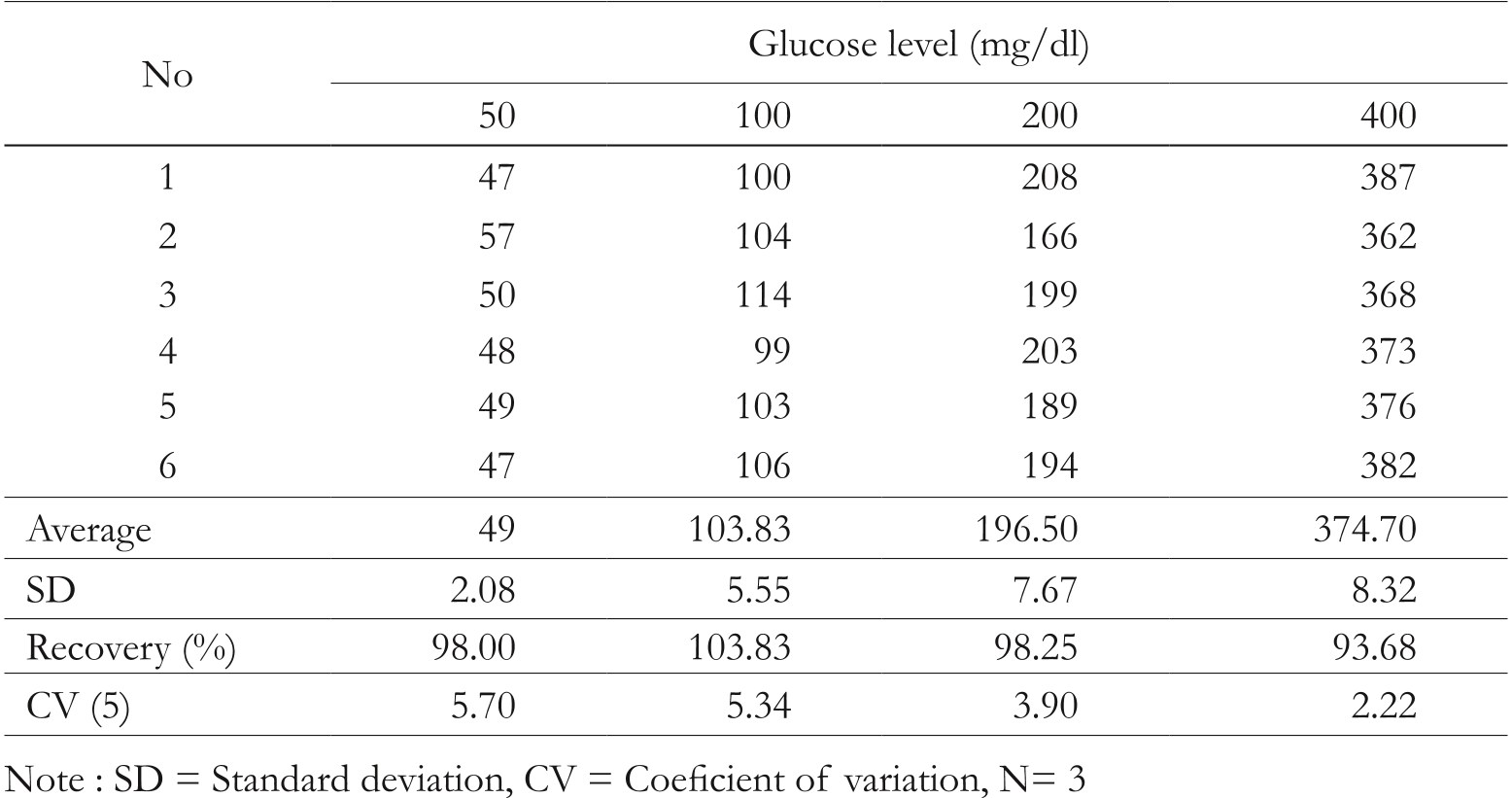
Table 2. Preliminary recovery of glucose level in blood of testing animals by Re...
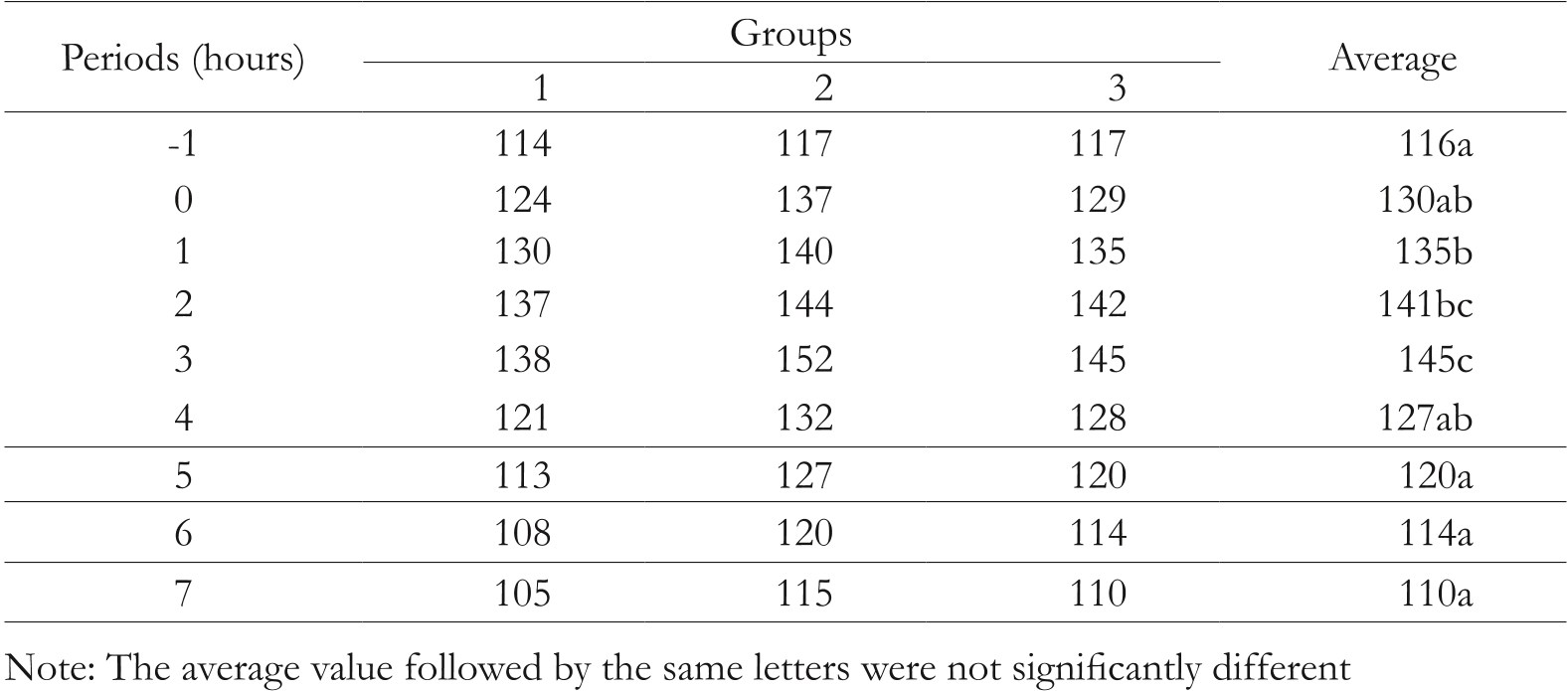
Table 3. Determination of the time interval of hyperglycemic condition in rat (m...
Paper Details
Title
Effect of Sappan Wood (Caesalpinnia sappan L) Extract on Blood Glucose Level in White Rats
Published Date
Jan 1, 2014
Volume
1
Issue
2
Pages
109 - 115
References9
Original paper
# 1MA Jafri(Jamia Hamdard)
4
# 2M. Aslam(Jamia Hamdard)
47
Last. Surender Singh(SVCP: Swami Vivekanand College of Pharmacy)
33
'Gulnar farsi', male abortive flowers of Punica granatum L., are used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in Unani medicine. Oral administration of its aqueous-ethanolic (50%, v/v) extract led to significant blood glucose lowering effect in normal, glucose-fed hyperglycaemic and alloxan-induced diabetic rats. This effect of the extract was maximum at 400 mg/kg, b.w.
Original paper
Antioxidant activity of Caesalpinia sappan heartwood was studied both by in vitro and in vivo models. The ethyl acetate, methanol and water extracts exhibited strong antioxidant activity as evidenced by the low IC50 values in both 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl hydrazyl (DPPH) and nitric oxide methods. The values were found to be less or comparable to those of ascorbic acid and rutin, the standards used. Administration of the successive methanol and water extracts at 50 and 100 mg/kg body weight given fo...
Original paper
# 1Hong‐Xi Xu(HKJC: Hong Kong Jockey Club)
64
# 2Song F. Lee(Dalhousie University)
20
Using a bioassay‐directed purification scheme, the active antibacterial principle from Caesalpina sappan was isolated and identified to be brasilin. This compound showed potent activity against antibiotic‐resistant bacteria, notably methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin‐resistant enterococci (VRE), multi‐drug resistant Burkholderia cepacia as well as a number of other bacteria. The minimal inhibitory concentrations ranged from 4 to 32 µg/mL. The results from time‐kill s...
Review paper
# 1Eko Baroto Walujo(LIPI: Indonesian Institute of Sciences)
8
Indonesia is not only rich in its biodiversity but it is also well known as a country with high diversity of ethnicities. Each ethnic group has extensive experienced in the utilization and conservation of biological and ecological diversity. This biocultural richness has provided ethnobotanical researchers with endless research opportunities. Ethnobotanical study has a long history in Indonesia and dates back to the early Dutch colonization period when Dutch explorers and naturalists recorded th...
Original paper
# 1Eun-Ju You(SNU: Seoul National University)
1
# 2Lee‐Yong Khil(SNU: Seoul National University)
16
Last. Chang-Kiu Moon(SNU: Seoul National University)
14
Increased hepatic glucose output is one of the major mechanisms of hyperglycemia in diabetic patients. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F-2,6-BP), a gluconeogenic intermediate, plays a critical role in hepatic glucose output by regulating gluconeogenesis and glycolysis in the liver. Brazilin, an active component of sappan wood (Caesalpinia sappan), decreases blood glucose in diabetic animals. In this study, the effect of brazilin on gluconeogenic intermediate production and enzyme activity were examin...
Review paper
# 1Euis Holisotan Hakim(ITB: Bandung Institute of Technology)
23
# 2Yana Maolana Syah(ITB: Bandung Institute of Technology)
24
Last. Didin Mujahidin(ITB: Bandung Institute of Technology)
9
In a drug discovery program to combat various diseases, many natural chemicals originating from Indonesian tropical plants including Moraceae and Dipterocarpaceae have been investigated in our laboratory. These family of plants are known as rich sources of stilbenoid type of compounds which have been shown to have various bioactivities, that are potentially important in cosmetic bioindustry. In the course of our search for bioactive natural products from plants, we were interested in the stilben...
Original paper
# 1Praptiwi Praptiwi(LIPI: Indonesian Institute of Sciences)
9
# 2Mindarti Harapini(LIPI: Indonesian Institute of Sciences)
3
Last. Ida Astuti(ISTN: National Institute of Science and Technology)
2
The objectives of this research were to determine the chemical components and the peroxide values of three Aglaia species (A. argentea Blume, A. silvestria (M. Roemer) Merr and A. tomentosa Teijsm & Binn). Phytochemical screening was done by Cuiley method, while peroxide values were determined by iodometri-titration on methanol, hexane, chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts. The result of phytochemical screening indicated that all of Aglaia species tested (three species) contained sterol and...
Original paper
# 1Chairul Chairul(LIPI: Indonesian Institute of Sciences)
14
New drug discovery from natural products (bio-prospecting) is not an easy works and takes time, big budget, human resources etc. some important approaches must be taken in order to get success. A preliminary observation of biologycally active components is impotant approach in order that more selective in collecting research materials in the field. This approach is purposed to pacilitate (make easier) the next step research process later in the laboratory level. Several Methods of preliminary ob...
1