Original paper
Human In Silico Drug Trials Demonstrate Higher Accuracy than Animal Models in Predicting Clinical Pro-Arrhythmic Cardiotoxicity
Abstract
Early prediction of cardiotoxicity is critical for drug development. Current animal models raise ethical and translational questions, and have limited accuracy in clinical risk prediction. Human-based computer models constitute a fast, cheap and potentially effective alternative to experimental assays, also facilitating translation to human. Key challenges include consideration of inter-cellular variability in drug responses and integration of...
Figures & Tables
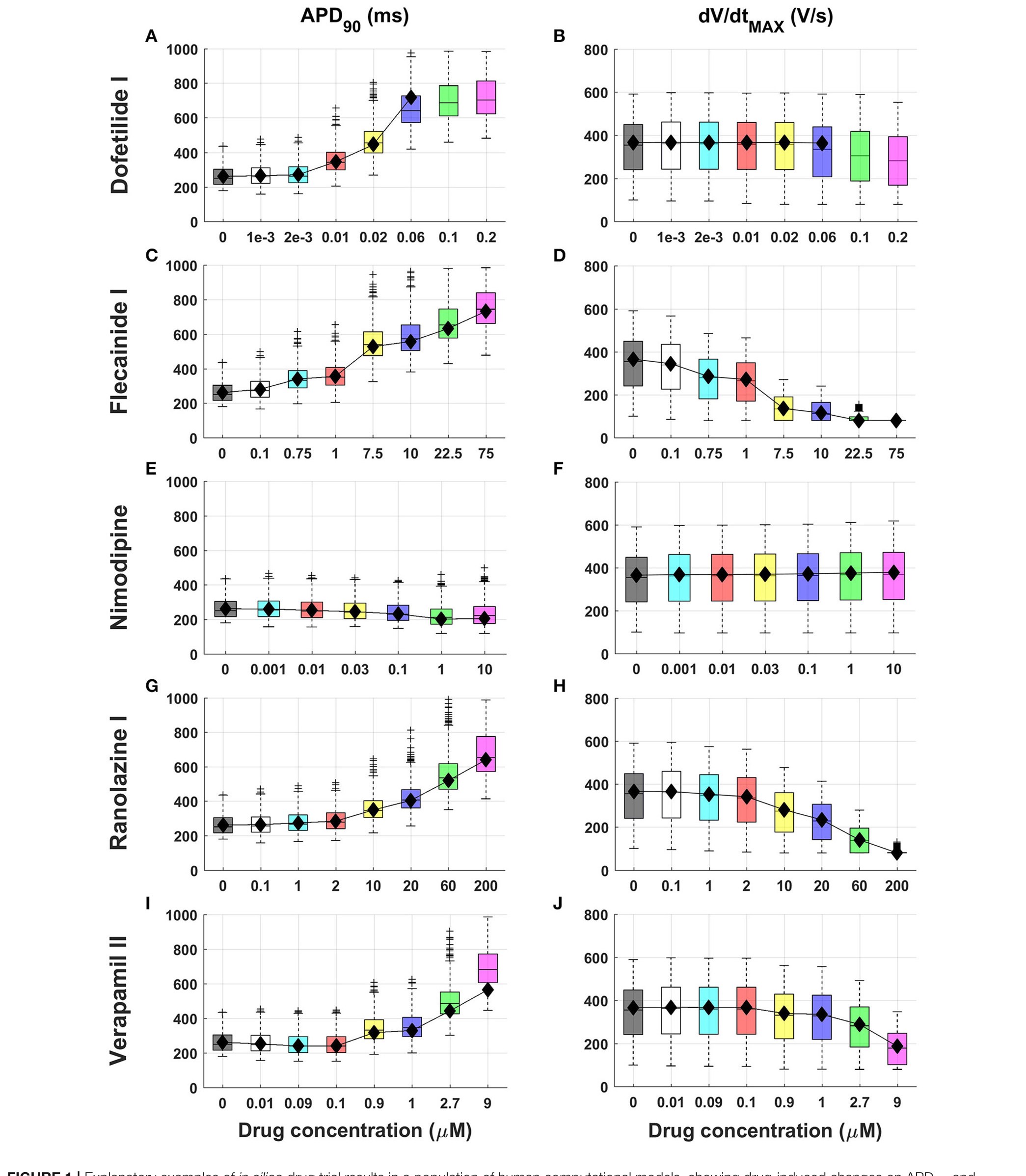
FIGURE 1 | Explanatory examples of in silico drug trial results in a population ...
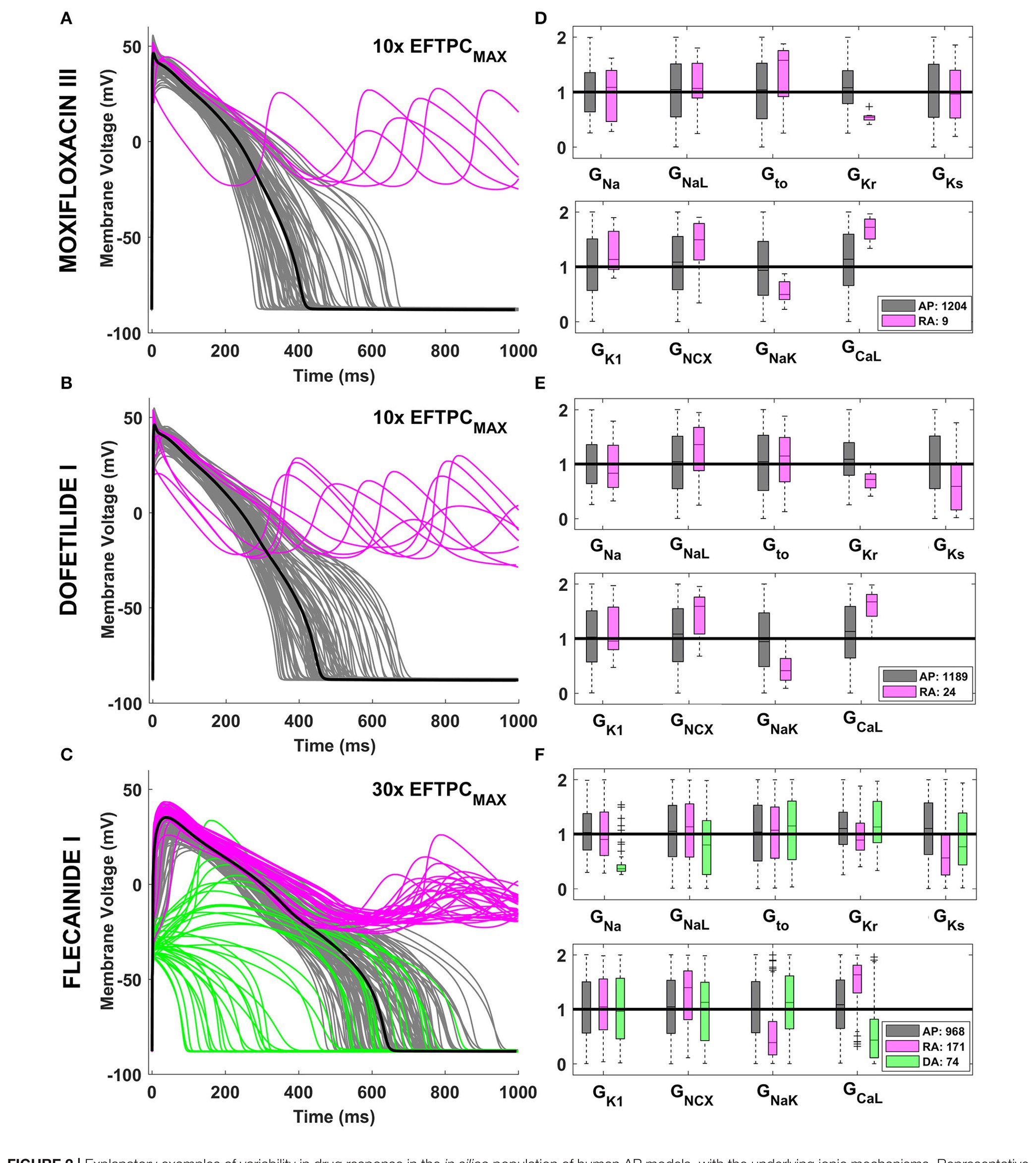
FIGURE 2 | Explanatory examples of variability in drug response in the in silico...
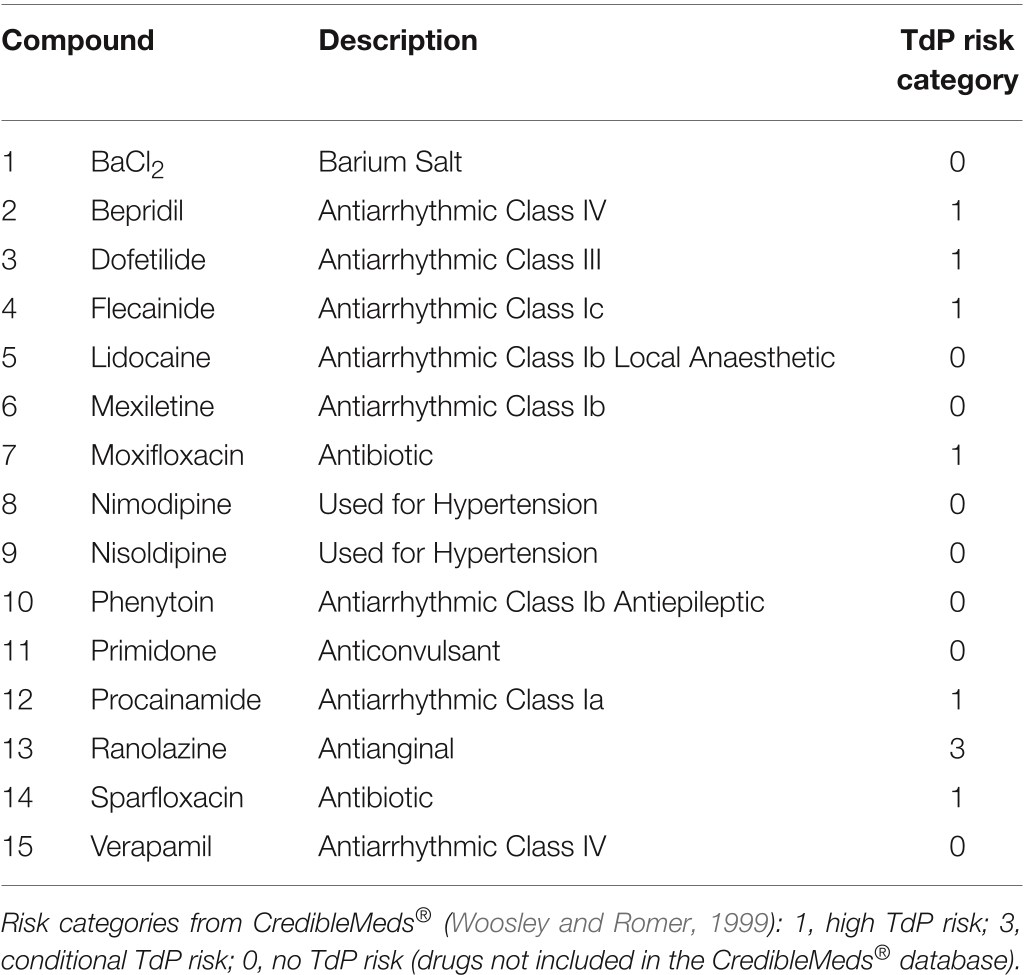
TABLE 1 | List of the 15 compounds considered for in silico drug assays comparis...
Paper Details
Title
Human In Silico Drug Trials Demonstrate Higher Accuracy than Animal Models in Predicting Clinical Pro-Arrhythmic Cardiotoxicity
Published Date
Sep 12, 2017
Journal
Volume
8
TrendsPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand a paper’s academic impact over time?
- Scinapse’s Citation Trends graph enables the impact assessment of papers in adjacent fields.
- Assess paper quality within the same journal or volume, irrespective of the year or field, and track the changes in the attention a paper received over time.
Citation AnalysisPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand the true influence of a researcher’s work across journals & affiliations?
- Scinapse’s Top 10 Citation Journals & Affiliations graph reveals the quality and authenticity of citations received by a paper.
- Discover whether citations have been inflated due to self-citations, or if citations include institutional bias.