Original paper
Digital Background Calibration for Pipelined ADCs Based on Comparator Decision Time Quantization
Volume: 62, Issue: 5, Pages: 456 - 460
Published: Jan 5, 2015
Abstract
This brief presents a digital background calibration technique that embraces comparator decision time to calibrate interstage gain errors and capacitor mismatches in pipelined analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). It does not modify the original analog signal path except for the addition of a comparator decision time binary quantizer built by simple digital gates. The technique does not limit either the ADC input signal swing or bandwidth....
Figures & Tables
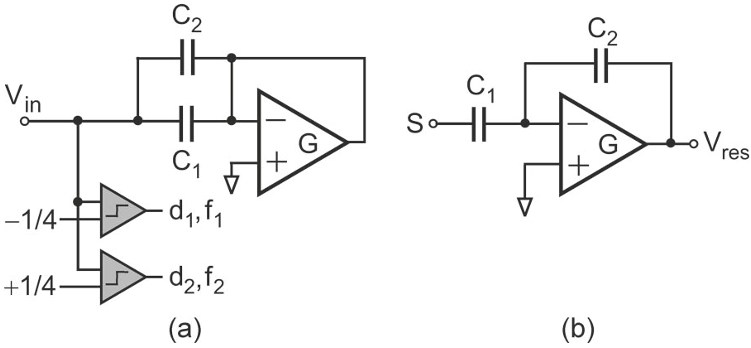
Fig. 1. 1.5-bit case. (a) Sampling phase. (b) Charge transfer phase.
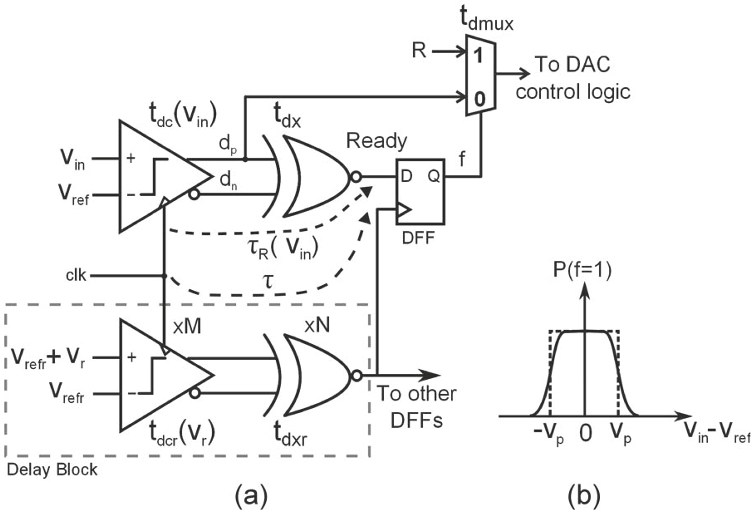
Fig. 2. (a) Schematic of a comparator with DTQ. Subscripted variable beside each...
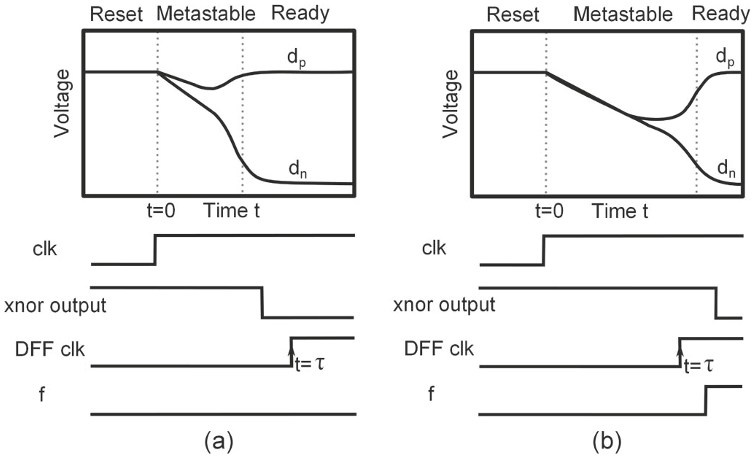
Fig. 3. Comparator and decision time quantizer waveforms for (a) large input and...
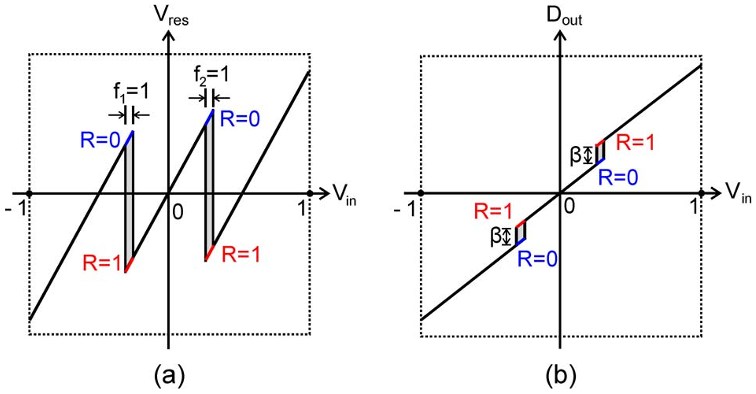
Fig. 4. 1.5-bit case. (a) Residue curve. (b) Transfer curve.
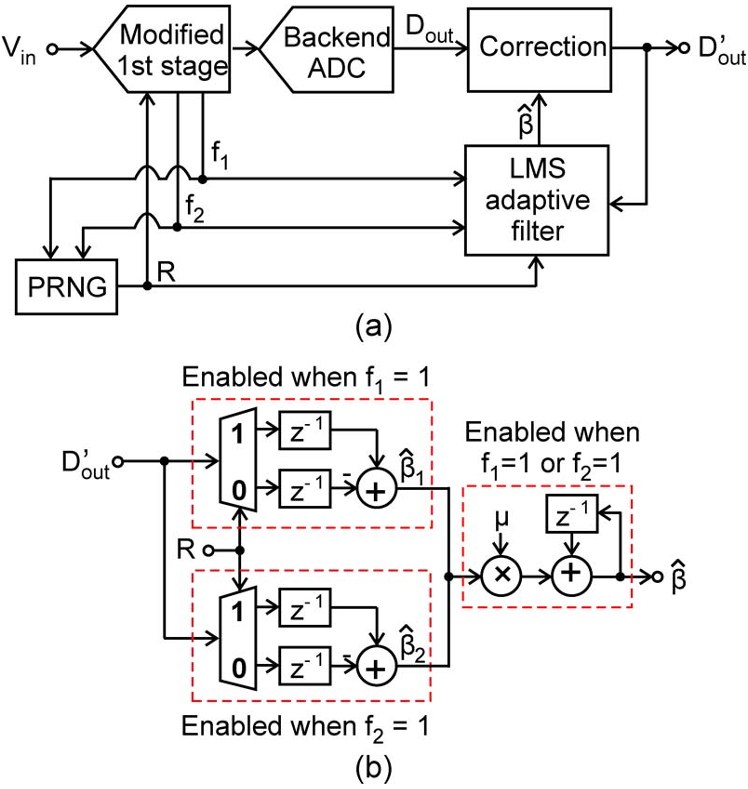
Fig. 5. (a) Main calibration architecture. (b) Detailed block diagram of the LMS...
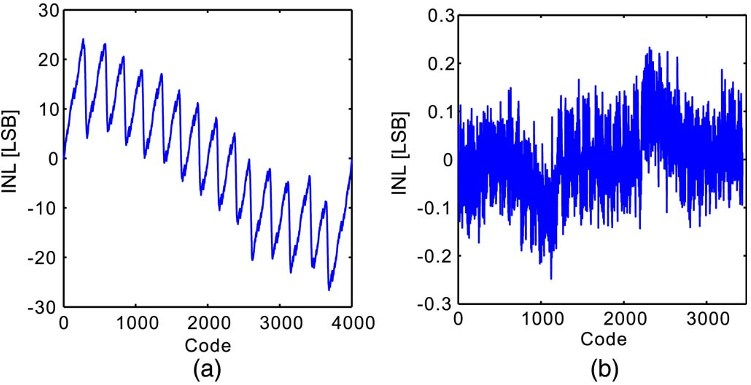
Fig. 6. 12-bit ADC INL. (a) Before calibration. (b) After calibration.
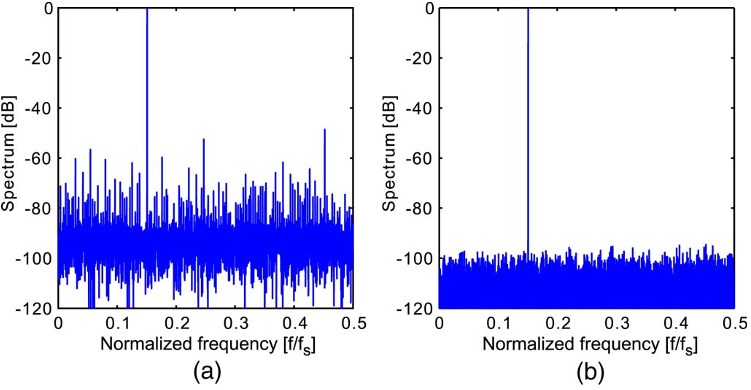
Fig. 7. ADC output spectra. (a) Before calibration. (b) After calibration.
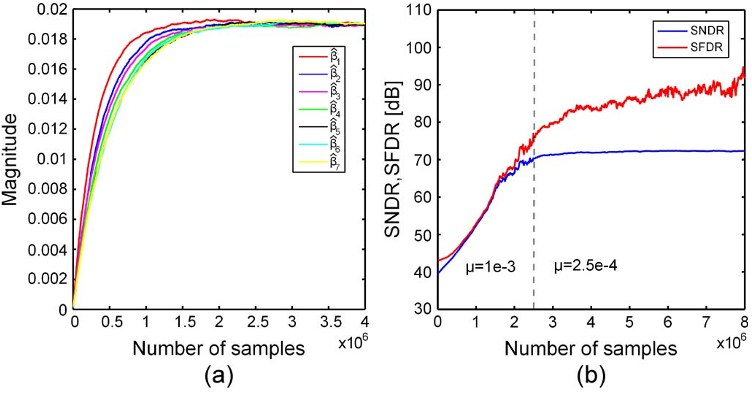
Fig. 8. Convergence of (a) β̂ of the first stage and (b) ADC SNDR/SFDR.
Paper Details
Title
Digital Background Calibration for Pipelined ADCs Based on Comparator Decision Time Quantization
Published Date
Jan 5, 2015
Volume
62
Issue
5
Pages
456 - 460
TrendsPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand a paper’s academic impact over time?
- Scinapse’s Citation Trends graph enables the impact assessment of papers in adjacent fields.
- Assess paper quality within the same journal or volume, irrespective of the year or field, and track the changes in the attention a paper received over time.
Citation AnalysisPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand the true influence of a researcher’s work across journals & affiliations?
- Scinapse’s Top 10 Citation Journals & Affiliations graph reveals the quality and authenticity of citations received by a paper.
- Discover whether citations have been inflated due to self-citations, or if citations include institutional bias.