Original paper
Fermentation of black tea broth (Kombucha): I. Effects of sucrose concentration and fermentation time on the yield of microbial cellulose
Abstract
The yield and properties of cellulose produced from bacterial fermentation of black tea broth (known as Kombucha) were investigated in this study. The tea broth was fermented naturally over a period of up to 8 days in the presence of sucrose. Tea broth with a sucrose concentration of 90 g/l produced highest yield of bacterial cellulose (66.9%). The thickness and yield of bacterial cellulose increased with fermentation time. The bacterial...
Figures & Tables
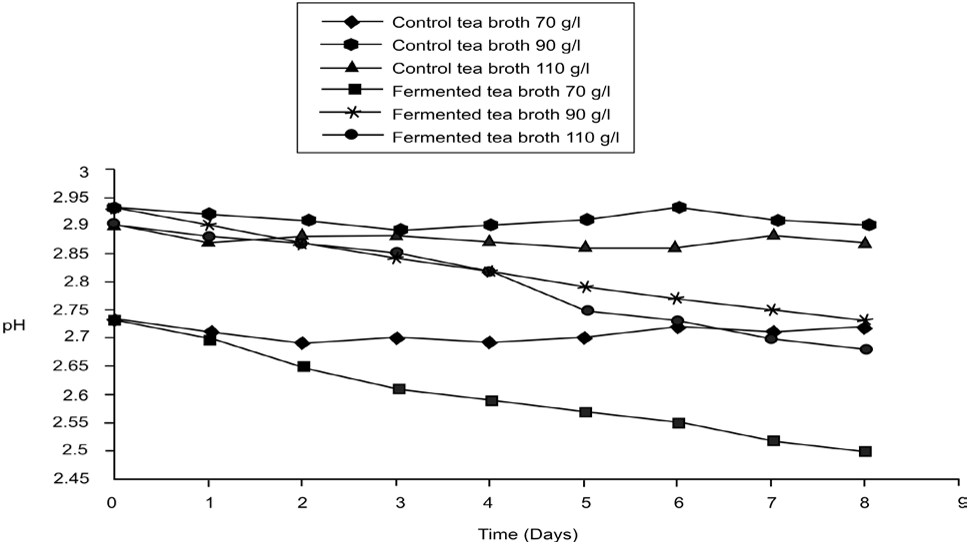
Figure 1. Changes in pH values for the fermented and control tea broths withdiff...
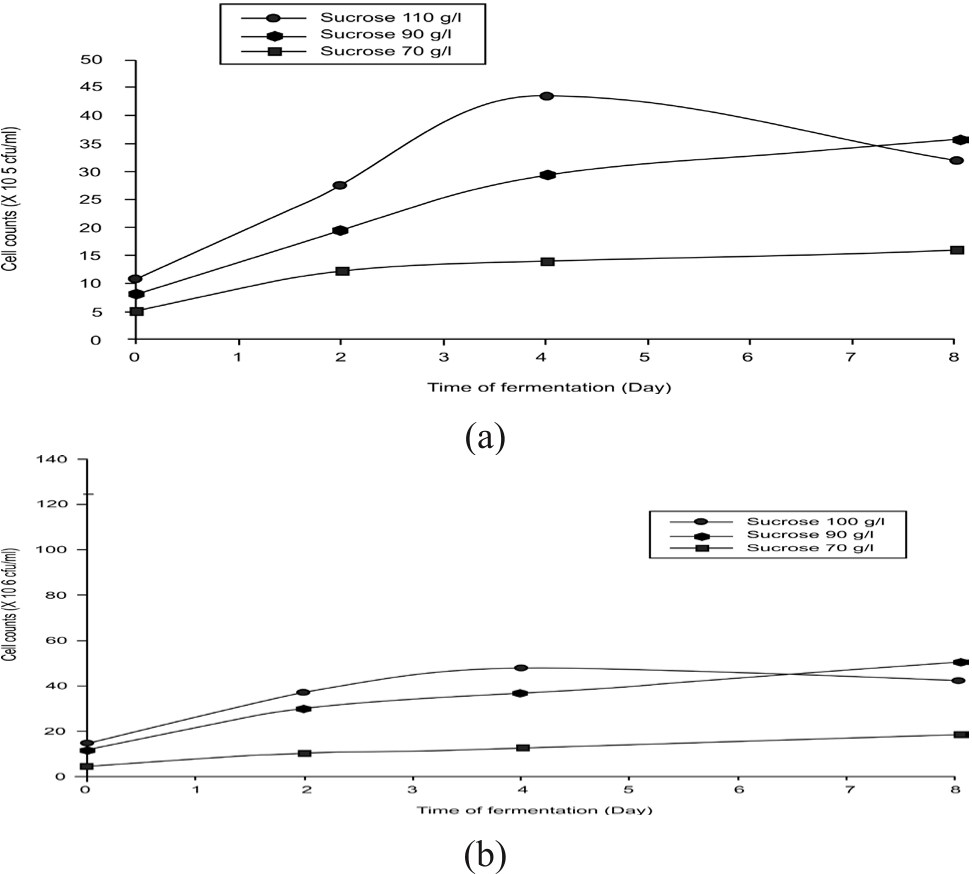
Figure 2. Changes in microbial counts for (a) acetic acid bacteria and (b) yeast...
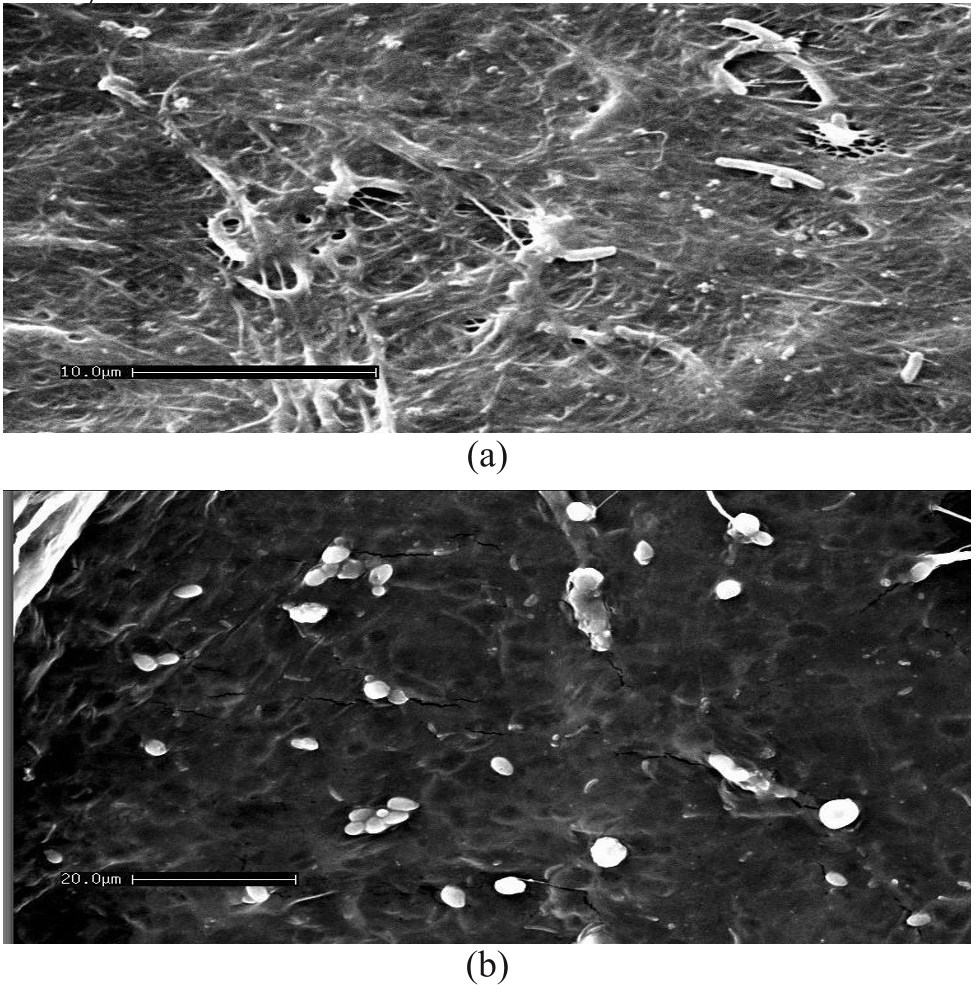
Figure 3. Scanning electron micrograph of (a) acetic acid bacteria (magnificatio...
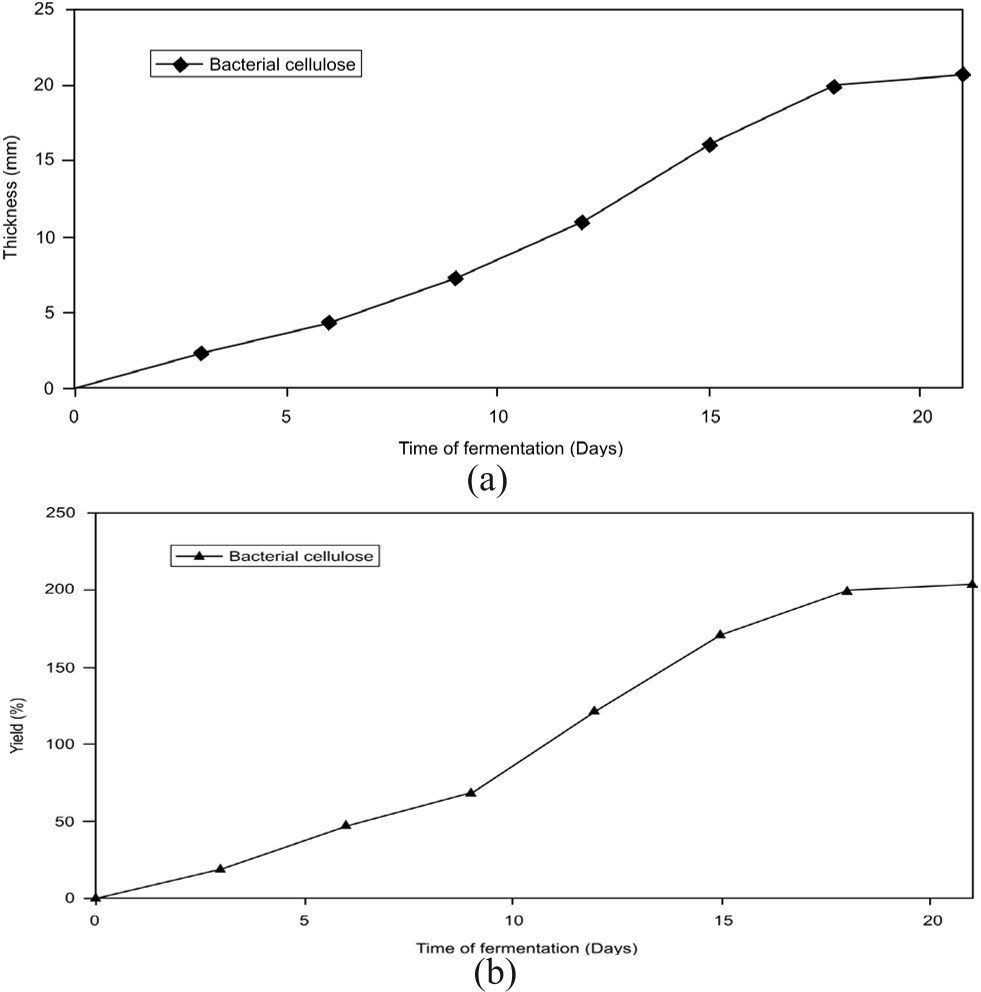
Figure 4. Changes in (a) thickness and (b) yield of bacterial cellulose during p...
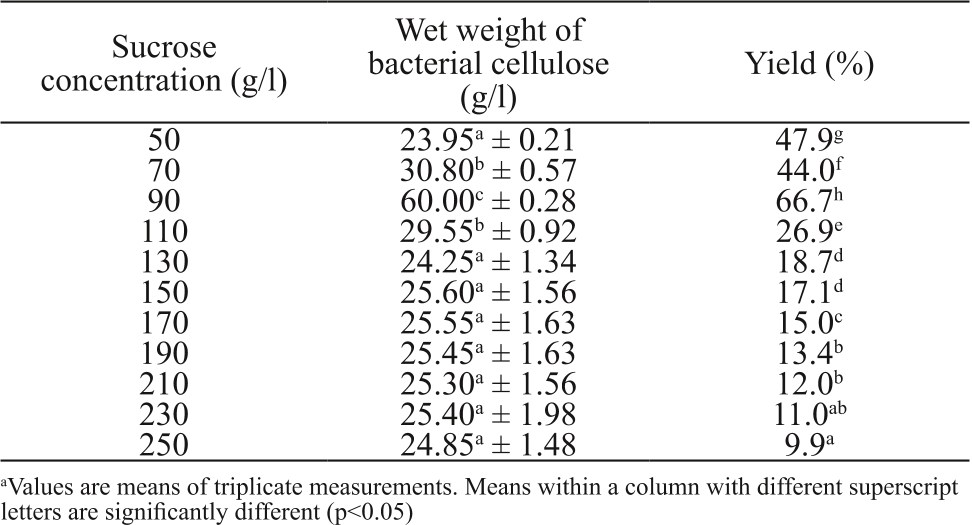
Table 1. Effect of different sucrose concentrations on the yield of bacterial ce...
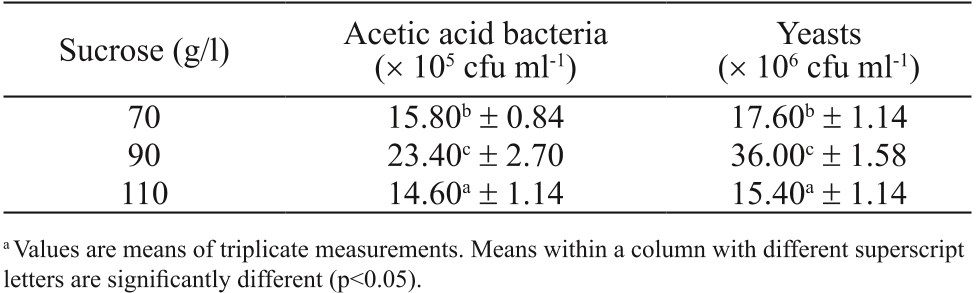
Table 2. Cell counts of acetic acid bacteria and yeasts of bacterial cellulose p...
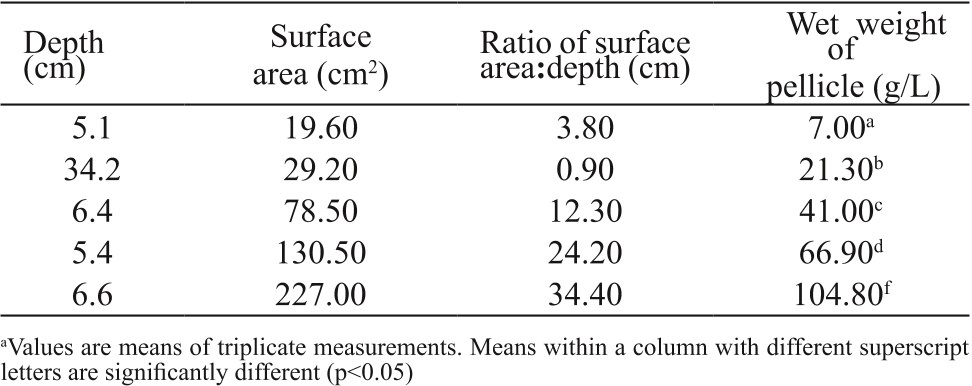
Table 3. Effect of culture surface area and depth on the bacterial cellulose pro...
Paper Details
Title
Fermentation of black tea broth (Kombucha): I. Effects of sucrose concentration and fermentation time on the yield of microbial cellulose
Published Date
Jan 1, 2012
Volume
19
Issue
1
Pages
109 - 117
Citation AnalysisPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand the true influence of a researcher’s work across journals & affiliations?
- Scinapse’s Top 10 Citation Journals & Affiliations graph reveals the quality and authenticity of citations received by a paper.
- Discover whether citations have been inflated due to self-citations, or if citations include institutional bias.