Original paper
A 53-nW 9.1-ENOB 1-kS/s SAR ADC in 0.13-$\mu$m CMOS for Medical Implant Devices
Volume: 47, Issue: 7, Pages: 1585 - 1593
Published: Apr 27, 2012
Abstract
This paper describes an ultra-low power SAR ADC for medical implant devices. To achieve the nano-watt range power consumption, an ultra-low power design strategy has been utilized, imposing maximum simplicity on the ADC architecture, low transistor count and matched capacitive DAC with a switching scheme which results in full-range sampling without switch bootstrapping and extra reset voltage. Furthermore, a dual-supply voltage scheme allows the...
Figures & Tables
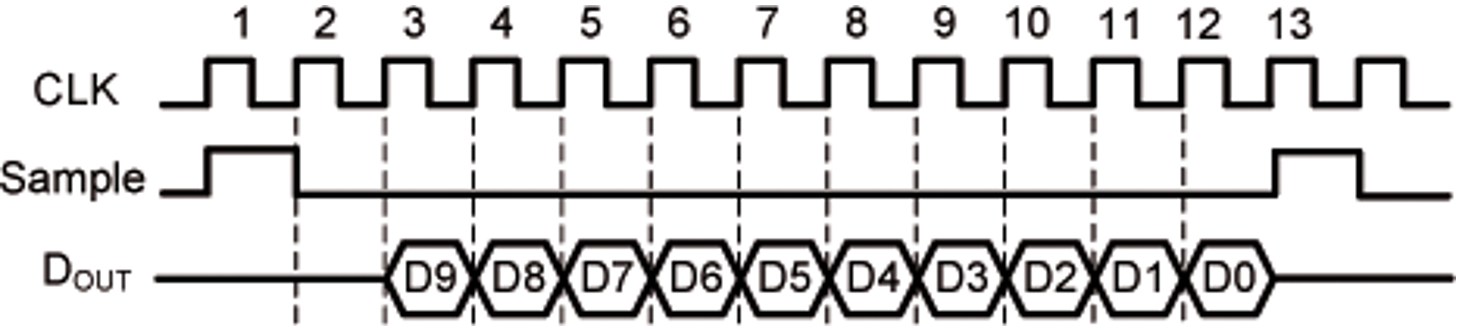
Fig. 10: Time sequence of the synchronous SAR control logic.
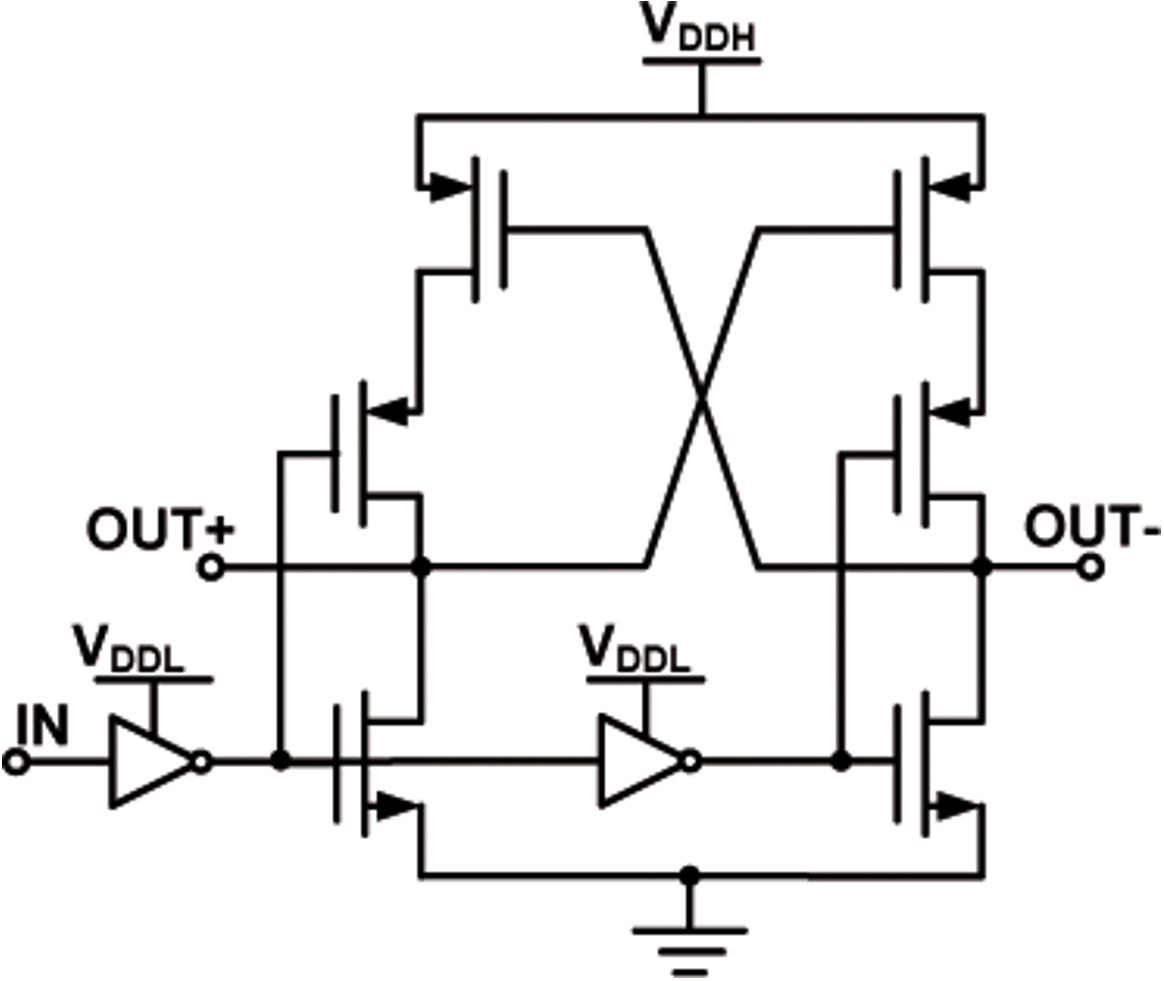
Fig. 11: Level shifter [26].
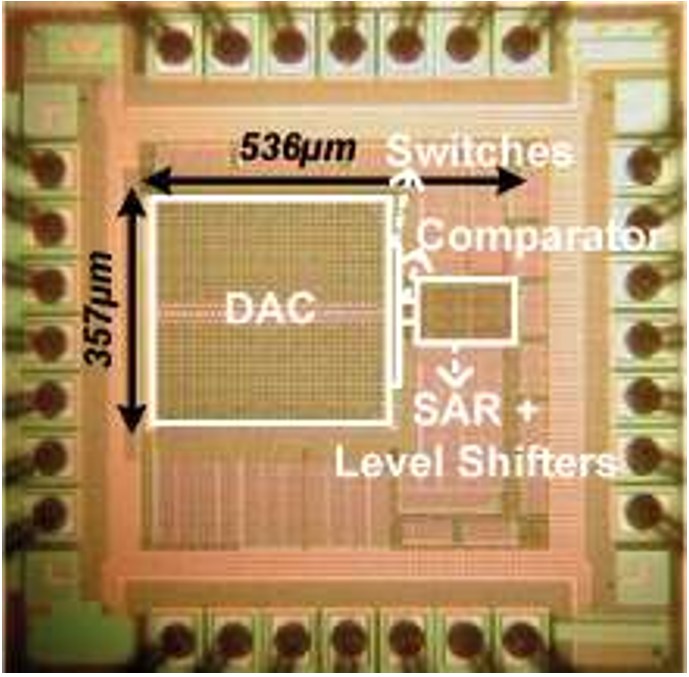
Fig. 12: Die photograph of the ADC in 0.13-μm CMOS technology. The SNDR of the A...
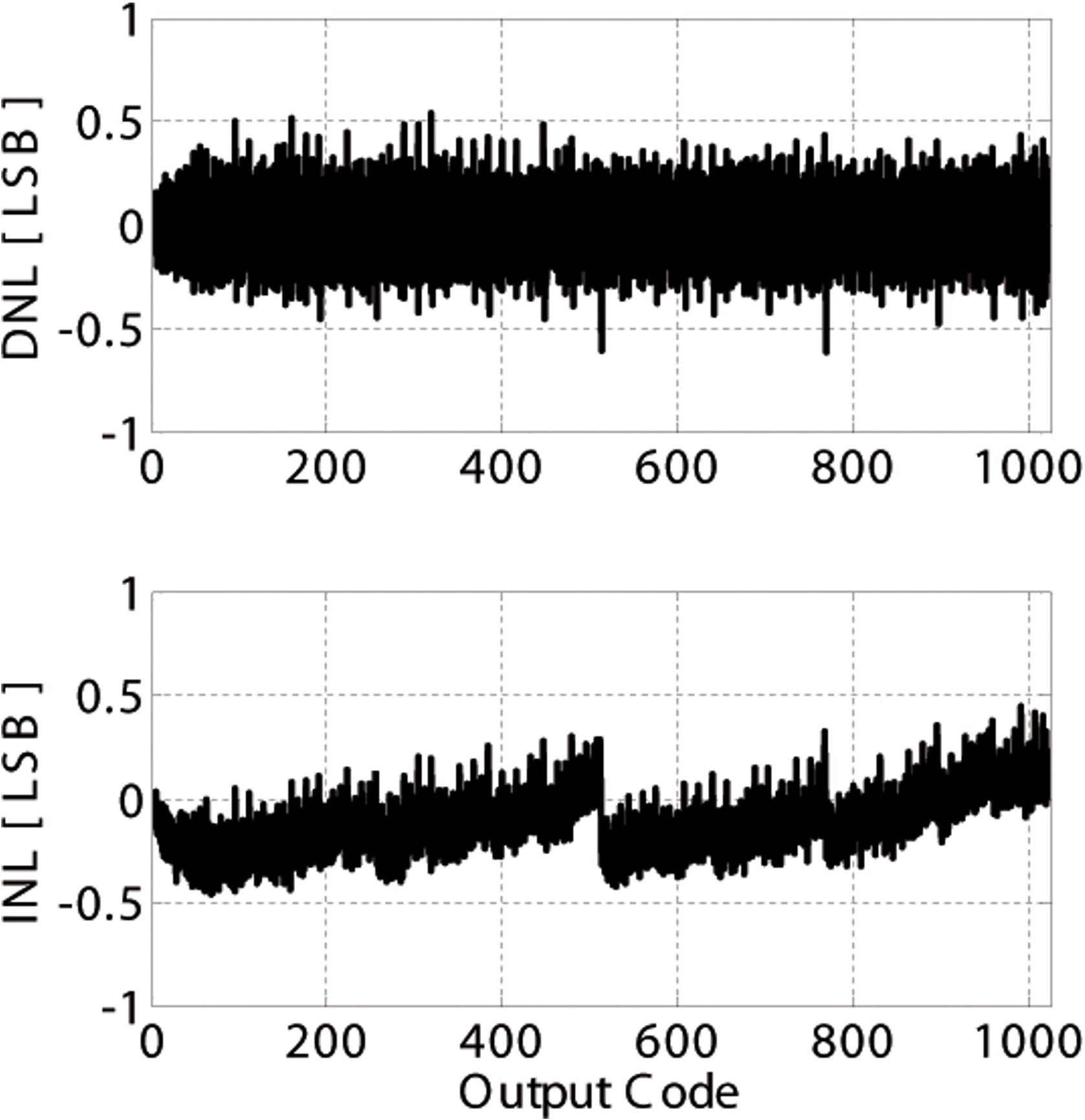
Fig. 13: Measured DNL and INL errors. Multiple supply voltage domains were utili...
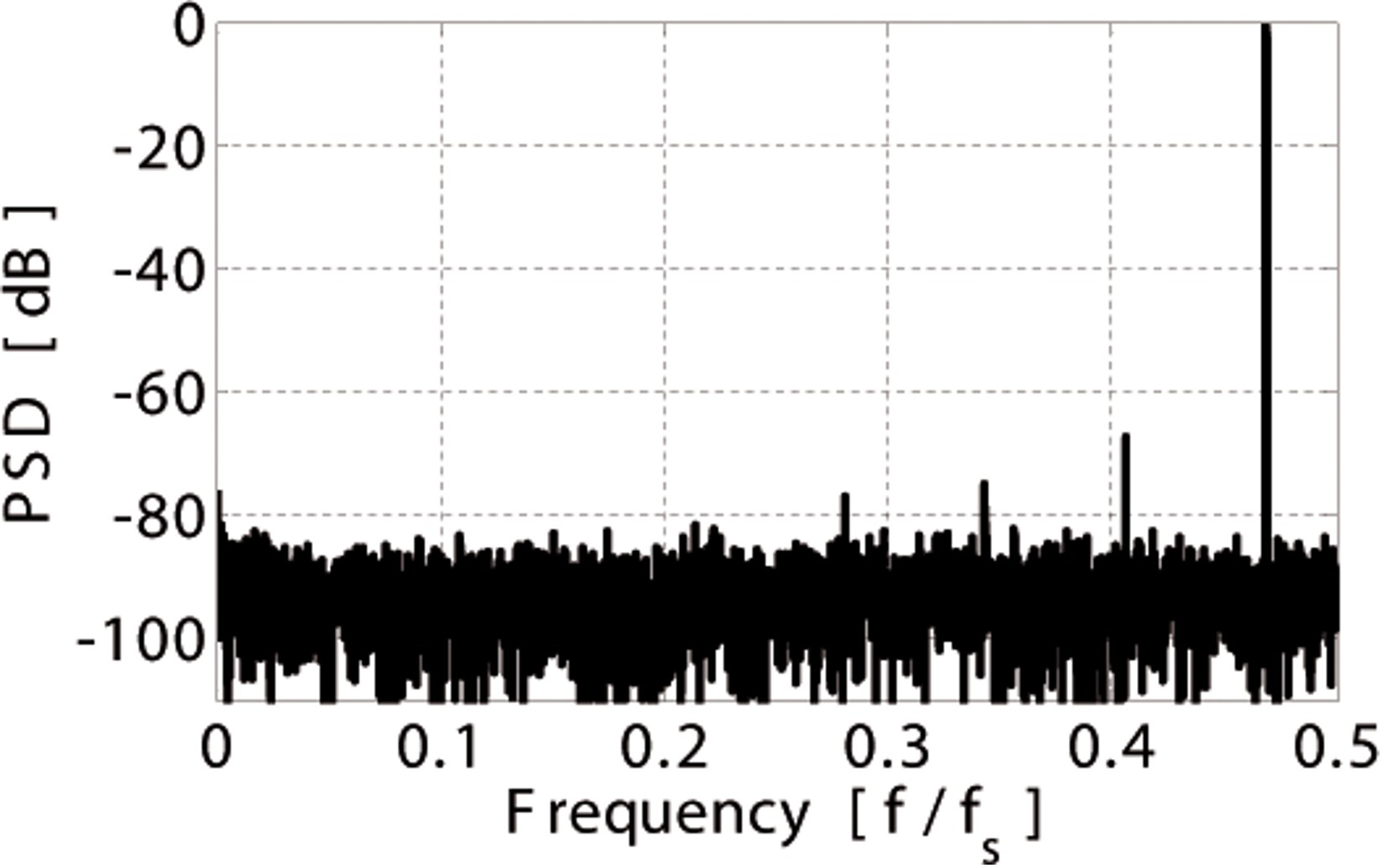
Fig. 14: Measured 8,192-point FFT spectrum at 1 kS/s.
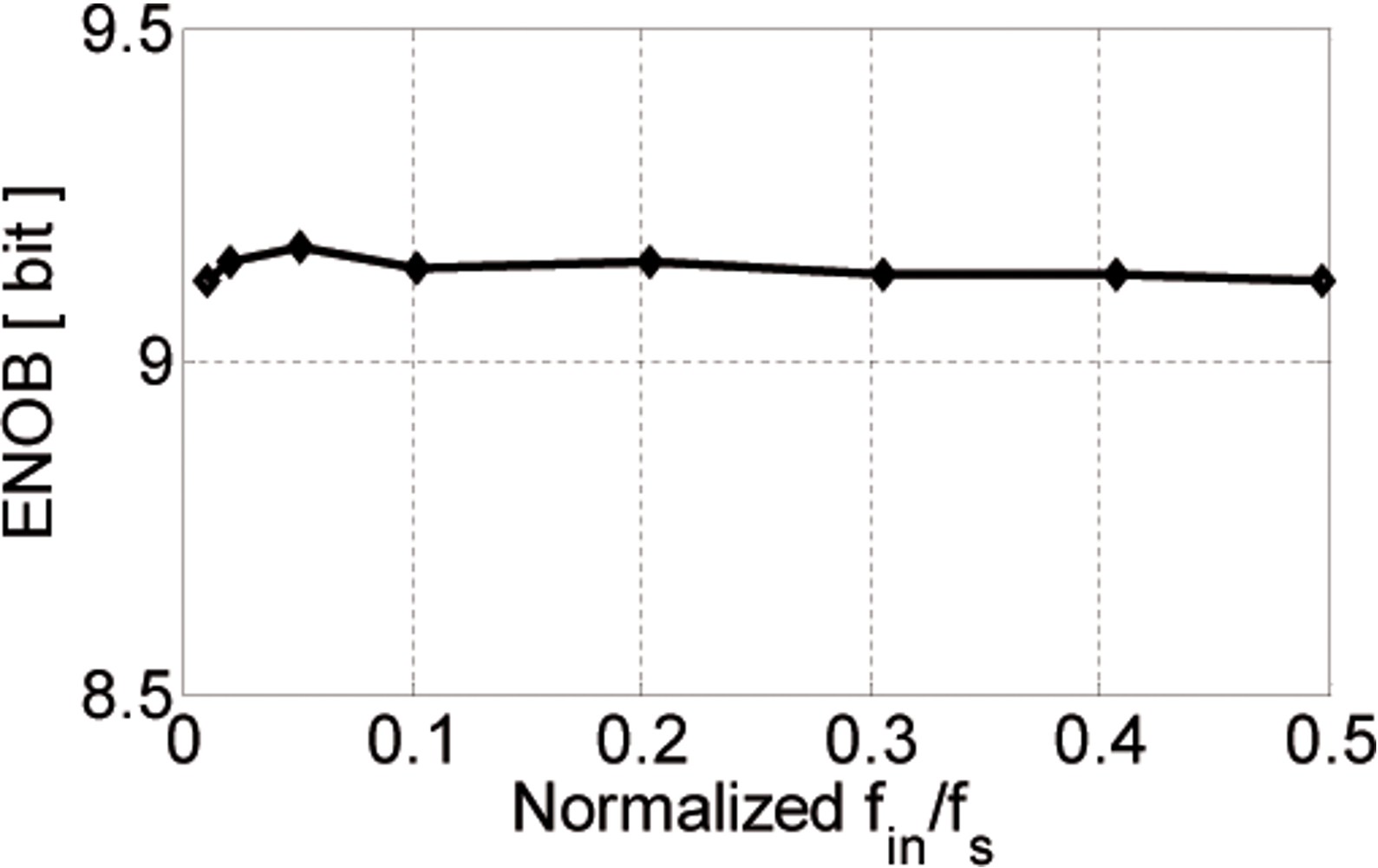
Fig. 15: ENOB of the ADC versus input frequency.
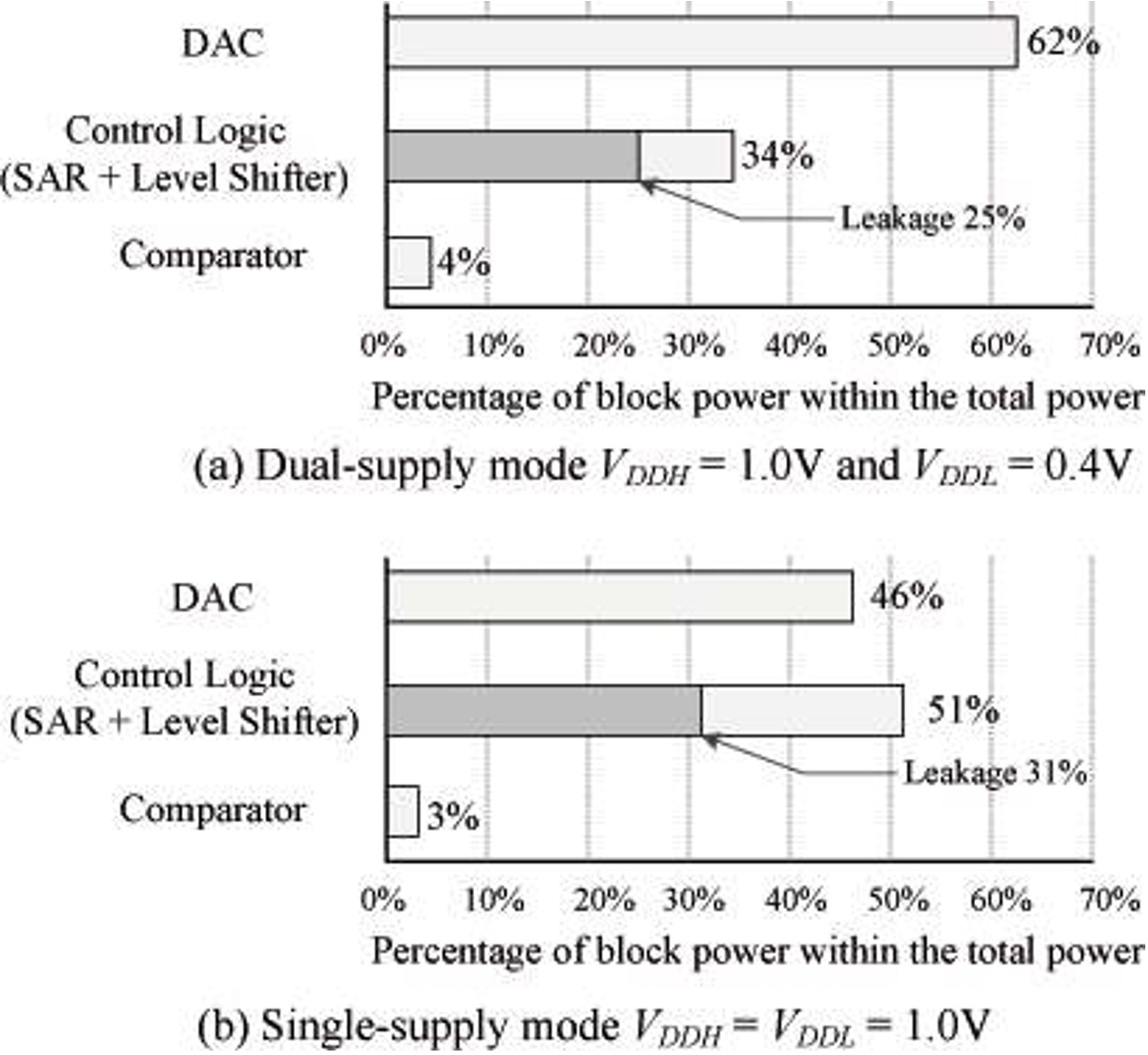
Fig. 16: The ADC power breakdown in dual and single supply modes, where the perc...
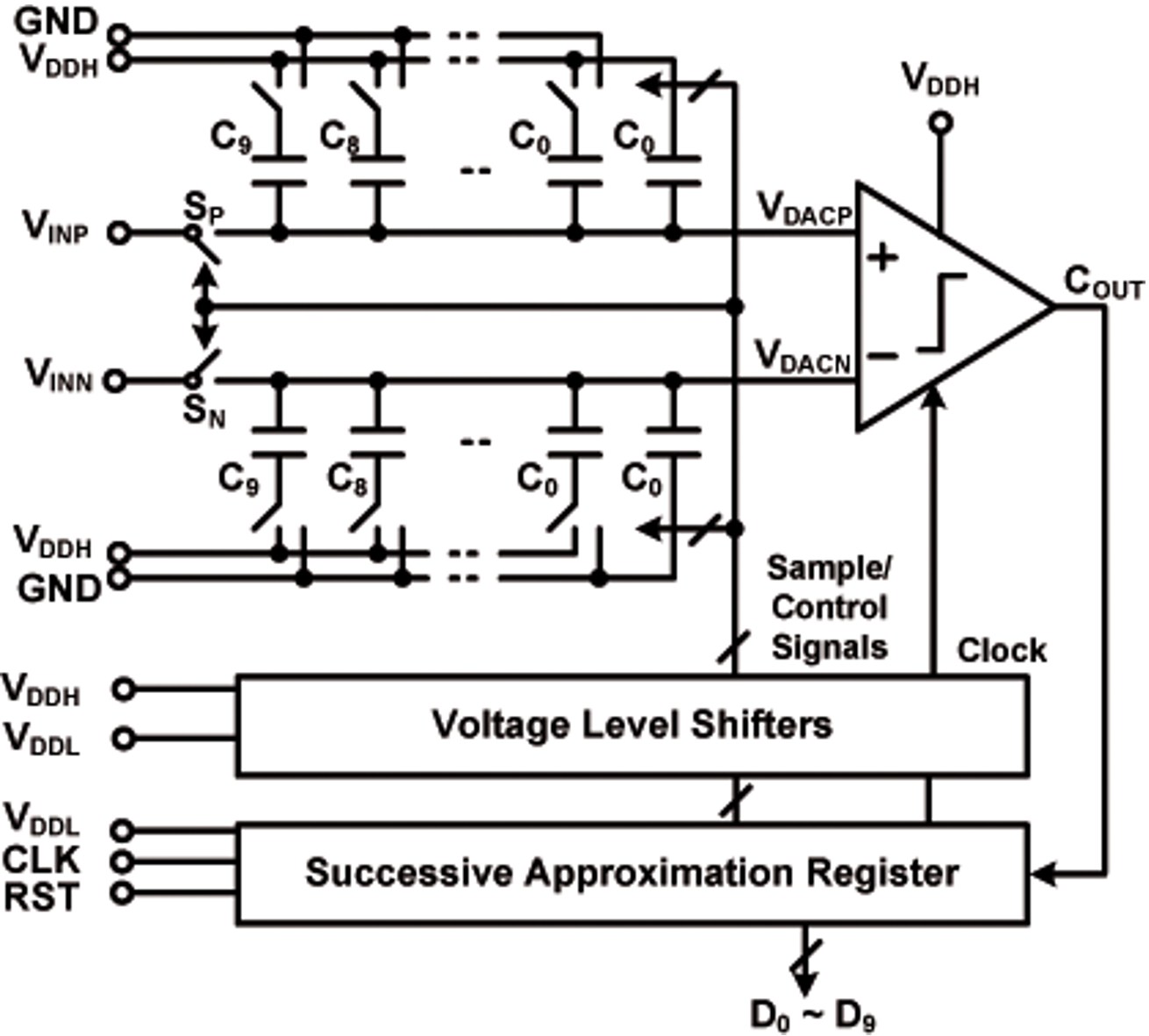
Fig. 2: Architecture of the SAR ADC.
Paper Details
Title
A 53-nW 9.1-ENOB 1-kS/s SAR ADC in 0.13-$\mu$m CMOS for Medical Implant Devices
Published Date
Apr 27, 2012
Volume
47
Issue
7
Pages
1585 - 1593
Citation AnalysisPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand the true influence of a researcher’s work across journals & affiliations?
- Scinapse’s Top 10 Citation Journals & Affiliations graph reveals the quality and authenticity of citations received by a paper.
- Discover whether citations have been inflated due to self-citations, or if citations include institutional bias.