Original paper
Rhodiola rosea in stress induced fatigue — A double blind cross-over study of a standardized extract SHR-5 with a repeated low-dose regimen on the mental performance of healthy physicians during night duty
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of repeated low-dose treatment with a standardized extract SHR/5 of rhizome Rhodiola rosea L, (RRE) on fatigue during night duty among a group of 56 young, healthy physicians. The effect was measured as total mental performance calculated as Fatigue Index. The tests chosen reflect an overall level of mental fatigue, involving complex perceptive and cognitive cerebral functions, such as...
Figures & Tables
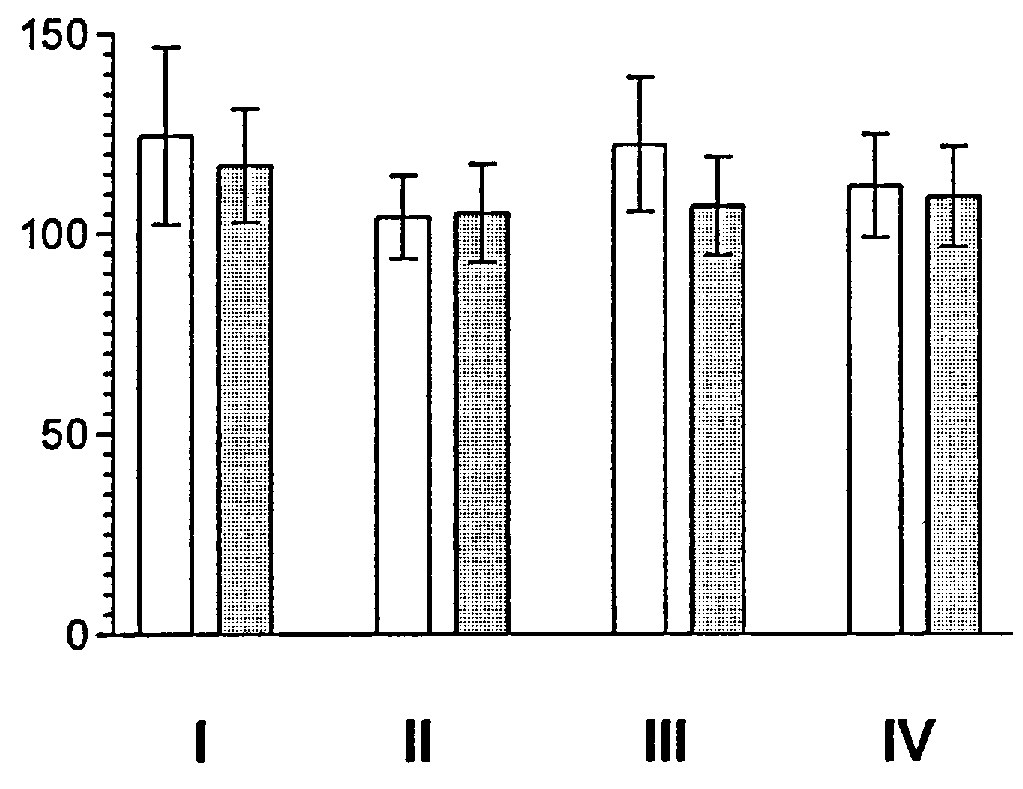
Fig. 1. Mean values of Fatigue indices and total index. (Value of scoring before...
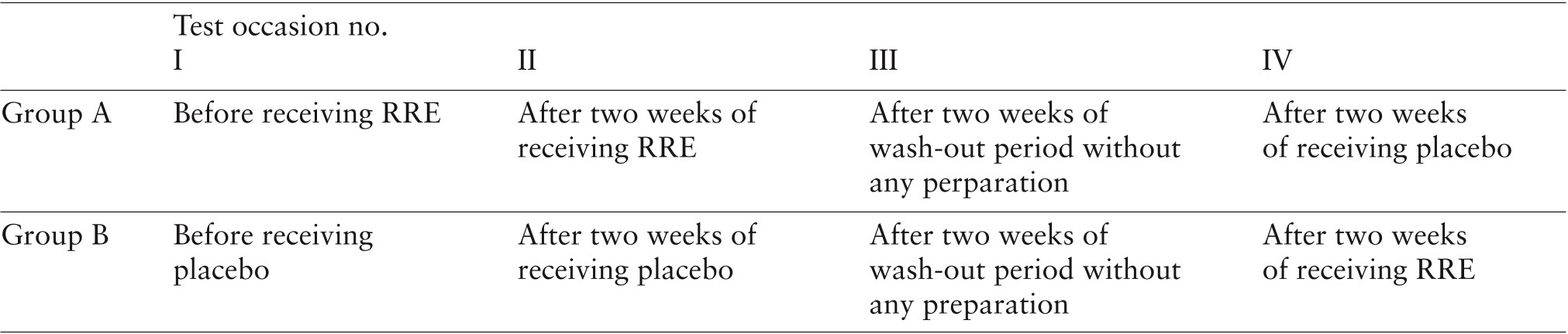
Table 1
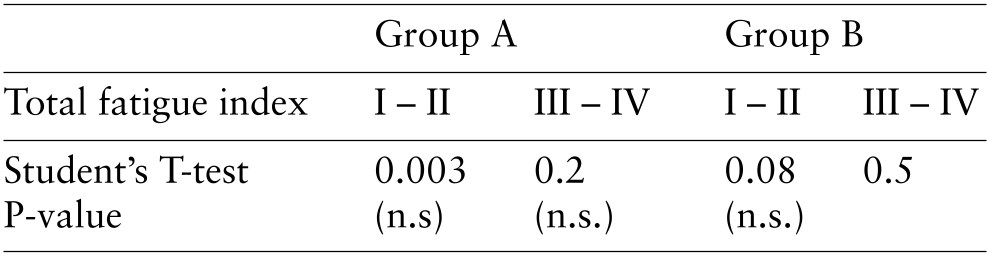
Table 2
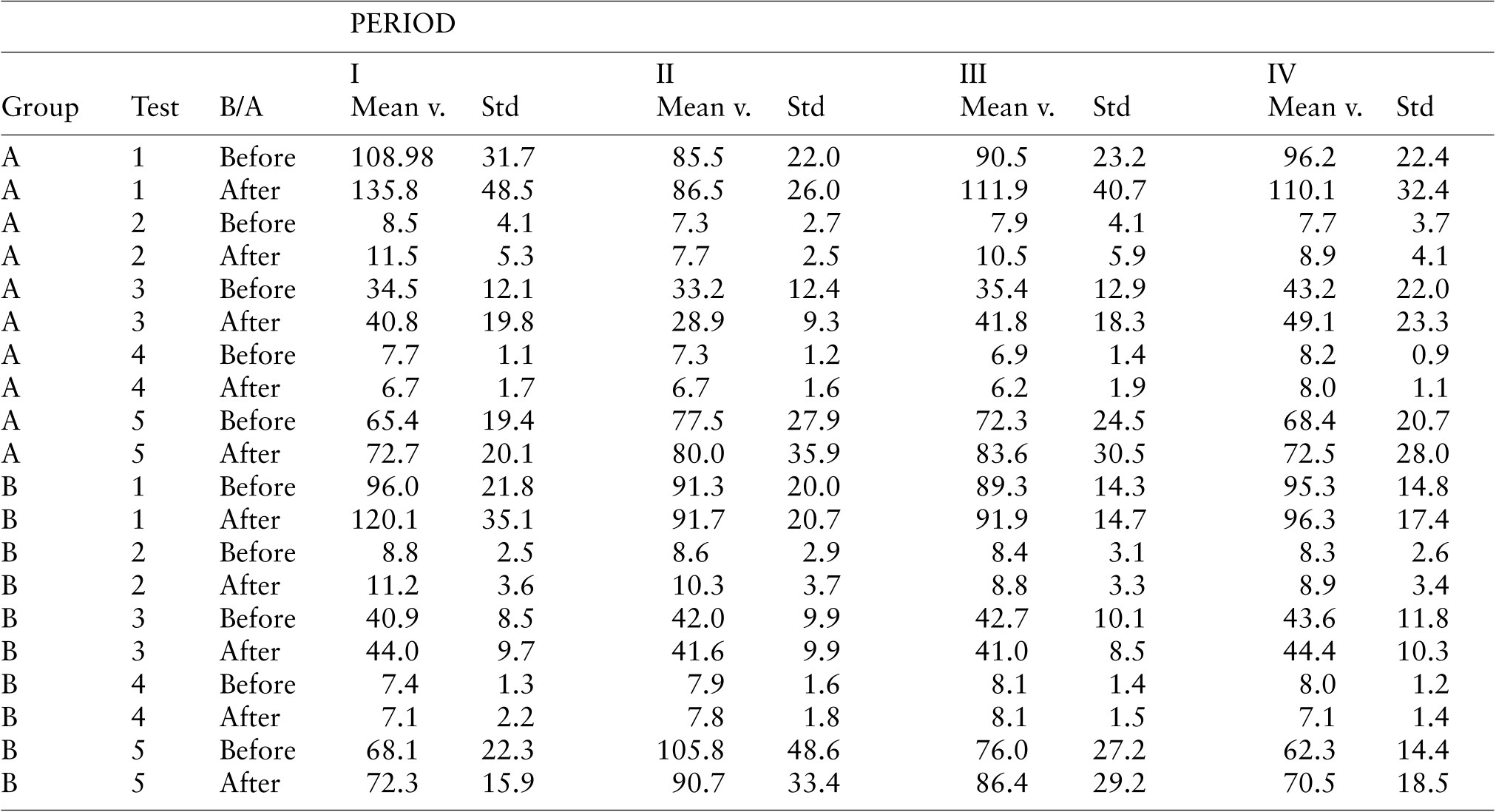
Table 3. Test scores: Mean values and standard deviations.
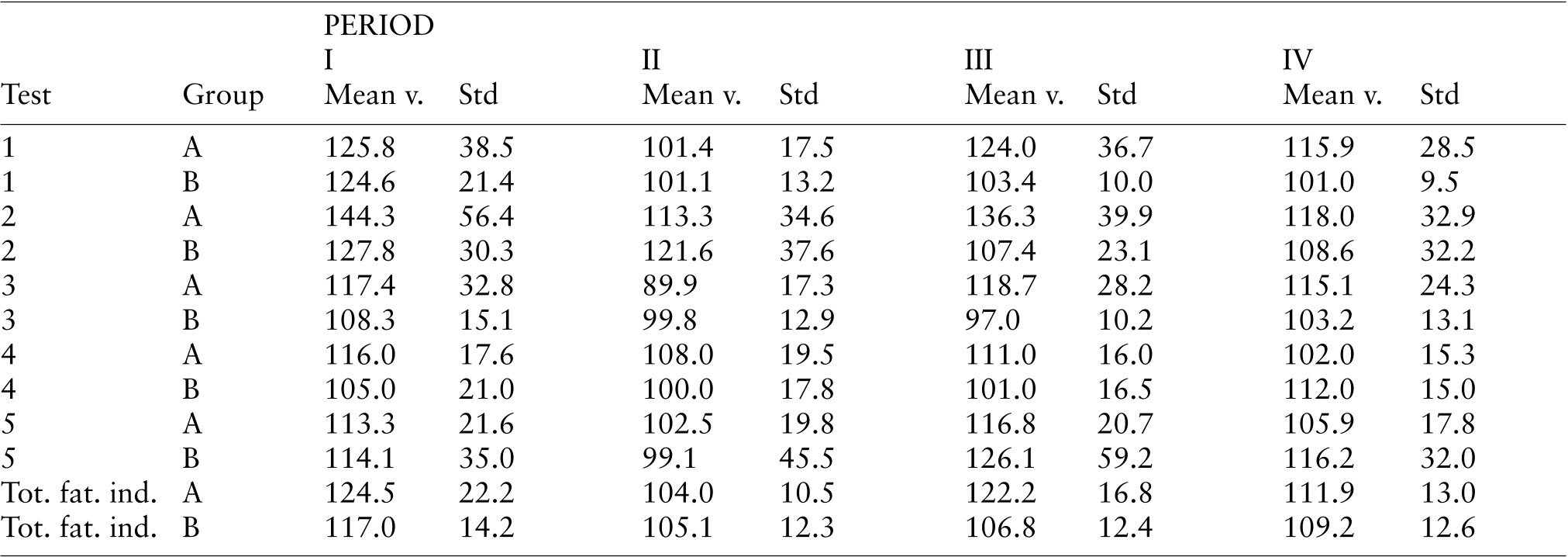
Table 4. Mean values of Fatigue indices and total fatigue index. (Value of scori...
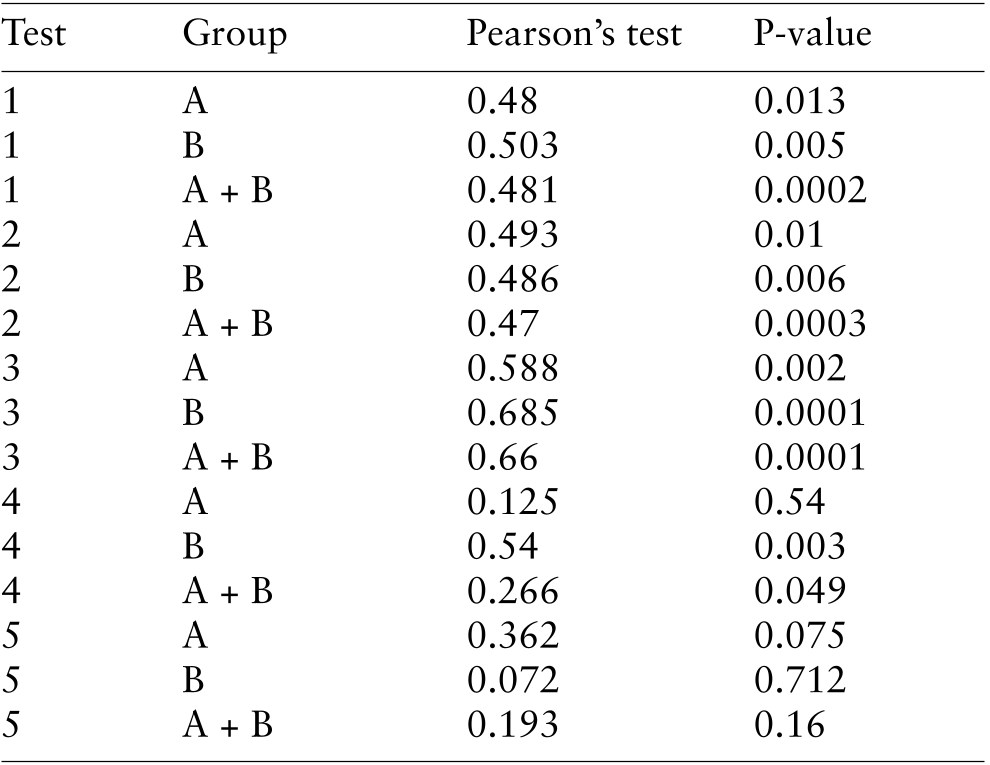
Table 5. Correlation between before-duty scores on occasion I and III.
Paper Details
Title
Rhodiola rosea in stress induced fatigue — A double blind cross-over study of a standardized extract SHR-5 with a repeated low-dose regimen on the mental performance of healthy physicians during night duty
Published Date
Oct 1, 2000
Journal
Volume
7
Issue
5
Pages
365 - 371
TrendsPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand a paper’s academic impact over time?
- Scinapse’s Citation Trends graph enables the impact assessment of papers in adjacent fields.
- Assess paper quality within the same journal or volume, irrespective of the year or field, and track the changes in the attention a paper received over time.
Citation AnalysisPro
You’ll need to upgrade your plan to Pro
Looking to understand the true influence of a researcher’s work across journals & affiliations?
- Scinapse’s Top 10 Citation Journals & Affiliations graph reveals the quality and authenticity of citations received by a paper.
- Discover whether citations have been inflated due to self-citations, or if citations include institutional bias.